AlB2, AlB12, Al4C3, Al3BC, Al8C7B4, K2CrO4, K2PbCl4, KPb2Cl5, Hg2Cl2, Na2MoO4, Na2CrO4, PbCl2.
The FactPS 8.4 exclusion file has been updated. The file is consulted when a given compound is listed in more than one database. For example MgSnO3, Mg2SnO4, Na2S2O7, ... (see above) are oxides that have been added to FactPS 8.4 and these compounds are also stored in FToxid. When FactPS and FToxid databases are selected, if a user selects say all solids in the Equilib Menu Window, the exclusion file will avoid a duplicate selection by only selecting the FToxid compounds. This is a simple example with oxides where the selection priority is obvious.
But when more than one FACT compound database is selected and it involves say metals, alloys, oxides, salts, etc. there is a priority among competing databases that may not be not so evident. This is where the exclusion file plays an important role in avoiding the duplicate selection of compounds.
In FactPS 8.4 there are 91 elements with a total of 5203 compounds (was 5038 in 8.3) and 7373 phases (was 7167).
The following compound has been added : Li2Nb2O6.
The following compound has been deleted : LiNbO3.
The following 125 compounds have been added to SGPS :
SGPS has been updated by converting
the latest SGTE database (SGSUB-2017) to FactSage format.
FTfrtz was introduced in FactSage 6.3 (2012).
It is used for the production of nitrate-based fertilizers, from hydrous to anhydrous conditions. It can also be used for calculating the thermodynamic properties and phase equilibria in the fertilizer products, and for some explosives.
The FTfrtz compounds and solutions contain data for 26 pure salts and 14 salt solutions based on the family of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3), ammonium di-hydrogen phosphate (NH4H2PO4), ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4). fertilizers with additions of their corresponding potassium salts (and in some cases sodium salts). The model covers the addition of roughly up to 50 wt.% water (H2O).
- minor modifications to the documentation (MAP vs DAP)
- automatic exclusion of N2(g) and several other N-containing gaseous
species (needed for calculations involving NH4NO3)
Al4C5 has been added, and those pure solid metallic compounds (except Al) and solid metallic solutions for which the data are considered to be out-of-date have been removed.
* The carbides (C4- anion) and carbonates (CO32- anion) have been added to the thermodynamic model for the
NaF-AlF3-CaF2-Al2O3 base system.
That is, a thermodynamic model is now available for the
Na+, AlV3+, AlIV3+, Al26+, Ca2+
// F-, O2-, C4-, CO32-, Va- system
{where AlV3+ is the 5-coordinated Al3+, AlIV3+
is the 4-coordinated Al3+, Al26+
represents the dimerized (F-bridged) Al3+, and Va- is an anionic vacancy for metal dissolution}.
The carbides and carbonates were added in order to model the solubility of Al4C3 in presence of dissolved metal
(at Al4C3(s) and Al4O4C(s) saturation) and the solubility of CO2(g), respectively,
in the NaF-AlF3-CaF2-Al2O3 base electrolyte.
At the anode, CO2(g) is evolved and dissolves partially in the bath in the form of carbonates.
The following reactions must be taken into account :
* The following stoichiometric compounds were added to the FThall Compound database :
Na2Ca3Al2F14(s), Na4Ca4Al7F33(s),
Ca12Al14F2O32(s), Na2Mg2Al3F15(s),
Na2CO3(s1, s2, s3, l), CaCO3(s1, s2, l), and Na2Ca(CO3)2(s1, s2).
* Bath: The density of the NaF-AlF3-CaF2-Al2O3-LiF-MgF2 electrolyte
as a function of temperature and composition has been modeled.
In the Menu Window of Equilib, select the FTHall-BathA liquid solution and check the box "include molar volumes".
In the Results Window, the density value (in gram/cm3) calculated from the model is displayed (in parentheses)
at the 2nd line of the block corresponding to the liquid phase.
A system density (in gram/cm3) that takes into account the available density data for all phases at equilibrium
(liquid + one or more solid phases) is displayed below the integral property table.
* Liquid metal: Volumetric properties (density) as a function of temperature were entered for the following pure
liquids in the "Liqu" liquid metal solution of the FThall database :
Al, Ca, Li, Mg and Na. The volumetric properties (density) as a function of temperature and composition were
entered for the Al-Mg binary liquid in the "Liqu" liquid metal solution of the FThall database.
In the Menu Window of Equilib, select the FThall-Liqu liquid solution and check the box "include molar volumes".
* Bath: The viscosity of the NaF-AlF3-CaF2-Al2O3-LiF-MgF2
electrolyte as a function of temperature and composition has been modeled.
In the Menu Window of Equilib, select the FThall-BathA liquid solution and check the box "include molar volumes".
(The viscosity model uses both the molar volume calculated from the density model and the
quadruplet mole fractions calculated from the thermodynamic model, in addition to the viscosity model parameters.)
In the Results Window, the viscosity value (in Pa.s) calculated from the model is displayed at the end of the
block corresponding to the liquid phase.
* Liquid metal: The viscosity of the Al-Mg binary liquid as a function of temperature and composition
has been modeled.
In the Menu Window of Equilib, select the FThall-Liqu liquid metal solution and check the box "include molar volumes".
LiF, NaF, MgF2(s1), Al4C3, Na3AlF6(s1), Na3AlF6(s2), Na5Al3F14, Na2LiAlF6(s1), Na2LiAlF6(s2), CaF2(s1), CaF2(s2), LiCaAlF6, NaCaAlF6(s1), NaCaAlF6(s2), NaCaAlF6(s3), Na2Ca3Al2F14, Na4Ca4Al7F33, Li2O, MgO, CaO, Al2O3(s1), Al2O3(s2), Al2O3(s3), Al2O3(s4), NaAl9O14, CaAl12O19.
LiF, NaF, MgF2, CaF2
The new database FTionx is devoted to ionic organics systems ("ionx" stands for "ionics").
Currently, there are only "ionic liquid" compounds (also referred to as "room temperature molten salts").
Ionic liquids have a low temperature of fusion (with a higher limit usually set arbitrarily to 100C), and consist of organic cations (which are large and asymmetric), and organic or inorganic anions.
Work is in progress on Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) systems.
The FTionx databases contain data for pure ionic organics compounds and ionic organic solutions of 8 cations:
with C3MIm = 1-propyl-3-methyl-imidazolium, C4MIm = 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium,
C3MPip = 1-propyl-1-methyl-piperidinium, C3MPy = 1-propyl-3-methyl-pyridinium,
C3MPyrr = 1-propyl-1-methyl-pyrrolidinium, C4MPyrr = 1-butyl-1-methyl-pyrrolidinium,
C2Py = 1-ethyl-pyridinium, and C4Py = 1-butyl-pyridinium.
and 6 anions:
In FTionx 8.4 there are currently:
For normal equilibrium calculations all the compounds tend to decompose into C(graphite, s) and gaseous products.
In order to inhibit these decomposition reactions
in FactSage, "virtual elements" (Qa, Qb, ..., Qh) with atomic weights of 0.0 have been used.
The total number of stored FTionx phase diagrams is 22.
For example, the following phase diagrams are polythermal projections of the liquidus surface.
FTlite was introduced in FactSage 6.1 (2009)
as a major expansion and update of the previous FSlite database for light metal
(mainly Al-based and Mg-based) alloys. The number of fully assessed binary and
ternary systems has more than doubled and a great many previous assessments
have been re-evaluated and re-optimized based upon the most recent data and
improved solution models.
The Mg-Al-Mn-Zn-Li-Ca-Sr-Ce-Y system has been completely re-optimized with the Modified
Quasichemical Model for the liquid phase for short-range ordering (solute-solute interactions).
Note that intermetallic ternary solid solutions are not completely evaluated in some subsystems.
The volumetric properties (density, molar volume) for the Mg-Al-Mn-Zn-(Fe) system (phases
in equilibrium with HCP_A3) are modeled: click the 'use molar volume' option in EQUILIB.
SiC alpha and beta have been changed (drastic change on metastable alpha, added thermal exp. to both).
Name of solid phases changed in Ce-Zn and Y-Zn binary systems.
The database has been updated. The changes are extensive and include the following:
The FTlite light metal alloy database represents a significant update and revision of the previous FTlite alloy database.
It is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Al alloys and Mg alloys.
Calculations involving Ti alloys and Li-Na-K mixtures can also be performed but not to the same extent as for Al- and Mg-alloys.
Al Alloys
Mg Alloys
A total of 622 binary systems (cf. 243 in the previous version of FTlite) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
For around 120 of these binary systems, only the liquid phase mixing parameters are stored.
Several dozen ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also been evaluated.
The database contains 200 solution phases and over 1400 pure compounds
(with more than 1700 stoichiometric phases counting allotropic forms).
All Mg-Zn-RE (RE = rare-earth elements) ternary systems have been evaluated from the Ph.D. thesis of Zhijun Zhu (Polytechnique Montreal).
Estimations of the density at 298.15K for most intermetallic phases (pure compounds) and of end-members of solutions.
Corrections of reported bugs for different solutions (NaZn13, CBCC_A12, etc.).
New documentation file (PDF) for the changes in the solution names between the 6.4, 7.0-7.1 versions.
Ca2Sn(s) has been added to the FTlite compound database.
FTlite 7.3 is a major update and restructure of the FACT light metal database.
It is primarilly designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving
Al alloys and Mg alloys.
Calculations involving Ti alloys and Li-Na-K-Mg-Ca-Sr-Ba mixtures
can also be performed but not to the extent as for Al- and Mg-alloys.
The database is intended to allow calculations over all ranges of composition,
although the assessed data are often most reliable for light metal rich composition ranges (Al-rich and Mg-rich compositions).
The database can be used for Al alloys in the commercial series 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, 5000, 6000 and 7000, and for a wide range cast alloys.
The table gives the list of optimized binary subsystems with the red, blue
and green elements given above.
The database is generally valid for the temperature range of approximately room temperature to 2200oC.
although for some alloys containing high melting point metals the data are reliable to still higher temperatures.
A total of 855 binary systems (was 781 in 7.2) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is given in the speadsheet shown here for the major and minor alloying elements of Al- and Mg-alloys.
Several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also been evaluated.
FTlite 7.3 contains 256 solution phases (was 200 in 7.2) and 1703 pure compounds (was 1400 in 7.2)
with 2104 stoichiometric phases including allotropic forms.
Extensive and detailed Tables listing the important solutions for calculations involving Al alloys, for solutions in Mg-alloys,
and a detailed list of all solutions are given in the documentation (78 pages total!)
The help section dealing with the selection of phases and species has been revised.
This important information now appears near the begining rather than at the end of the documentation file.
Minor update: - there is a correction to the volumetric properties of the Ag(fcc) pure substance
in the compound database (s1) and to the FCC_A1 phase in the solution database.
FTlite is primarily designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving
Al alloys and Mg alloys.
Calculations involving Ti alloys and Li-Na-K-Mg-Ca-Sr-Ba mixtures
can also be performed but not to the extent as for Al- and Mg-alloys.
Solid nitrides 24 phases:
h-BN, BN_S2, h-AlN, AlN_S2, AlN_S3, TiN, ZrN, InN, GaN, WN_S1, WN_S2, VN, TaN_S1, TaN_S2, Si3N4, NbN, Mn2N, Mn4N, Fe2N, Cr2N, CrN, CoN, CoN3, Nb2N
Solid borides 55 phases:
ZrB2, TiB2, HfB2, NbB2, NiB, Ni3B, ZrB12, ZrB, WB_S1, WB_S2, V3B4, VB, VB2, V2B3, V3B2, Ti3B4, TiB, NbB, Nb5B6, Ni2B, Ni4B3, Nb3B4, Nb2B3, Nb3B2,
NbB2, Mn2B, MnB4, Mn3B4, MnB, MnB2, Fe2B, FeB, Fe3B, CrB, Cr3B4, CrB2, CoB, Co2B, Co3B, AlB2,
BaB6, CaB6, Cr2B, Cr5B3, CrB4, KB6, LiB3, MgB2, MgB4, MgB7, NaB15, SrB6, W2B, AlCr2B2, AlCr3B4,
FTlite 8.2 is a major update of the database.
A total of 932 binary systems (vs 864 in 8.1) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
Several dozen ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also
been evaluated.
FTlite 8.2 contains 289 solution phases (vs 261 in 8.1) and 2064 pure compounds
(vs 1774 in 8.1) with 2175 stoichiometric phases counting allotropic forms.
In addition the volumetric properties (density @298.15 K, thermal expansion and compressibility B')
and thermal conductivities have been entered for the following solid compounds
(124 additions):
Complete details on FTlite 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in the
updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
In FTlite 8.3, a total of 992 binary systems (was 932 in 8.2)
have been evaluated, for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is shown here
for the major and minor alloying elements of Al-, Mg- and Ti-alloys.
Several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also
been evaluated.
FTlite 8.3 contains 317 solution phases (vs 287 in 8.2) and 2145 pure compounds
(was 1926 in 8.2) with 2621 stoichiometric phases counting allotropic forms (2374 in 8.2).
The total number of stored FTlite phase diagrams is now 1045 (was 982 in 8.2).
Complete details on FTlite 8.3 including all the phase diagrams are given in the
updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FTlite is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving
Al alloys, Mg alloys and Ti alloys.
It can also be used to perform calculations involving mixtures of Li-Na-KMg-Ca-Sr-Ba
with several other elements.
In FTlite 8.4 the changes are extensive.
A total of 1017 binary systems (was 992 in 8.3)
have been evaluated, for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
Several binary systems were revised.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is shown here
for the major and minor alloying elements of Al-, Mg- and Ti-alloys.
Several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also
been evaluated.
FTlite 8.4 contains 324 solution phases (vs 317 in 8.3) and 2304 pure compounds
(was 2145 in 8.3) with 2806 stoichiometric phases counting allotropic forms (2621 in 8.3).
The total number of stored FTlite phase diagrams is now 1077 (was 1045 in 8.3).
Complete details on FTlite 8.4 including all the phase diagrams are given in the
updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
Corrections have been made to the liquid Sn, FTmisc-Snlq phase.
The FTmisc-Felq liquid iron phase has been updated in FactSage 6.1; it is no longer identical to the liquid iron phase in the FSstel database. This phase is better suited for calculations involving iron and steelmaking processes, whereas the liquid iron phase in the FSstel database is better suited for calculations involving solidification of alloys.
Minor corrections have been made to the database for the Fe-S system
Changes in phase names in FTmisc :
Addition of the (Mn,Fe,Ca,Mg,Cr)S phase with the rocksalt structure for calculations of inclusions in steels in combination with the FToxid-slag phase.
The precise conditions for option 'I' phase selection (sulphide systems) are now stored within the FTmisc database
- the selection of '+' or 'I' will be done for you.
Many new calculated phase diagrams have been added to the documentation for FTmisc.
All compounds and solutions of the former "Light Metals' subsection of FTmisc have been removed.
(These include the solutions FTmisc-LMLQ, FTmisc-FCC, FTmisc-BCC, FTmisc-AlMg and FTmisc-MgSS,
and the stoichiometric compounds Al8Mg5, Al29Mg21, Mg2Si, MgC2, Mg2C3, Al4C3 and SiC.)
These data are out-of-date and have been superseded by the data in the FTlite (and FSlite) database.
The FTmisc databases contain data for
sulfides, alloys, etc.
In FTmisc 8.2
the MAT2 liquid sulfide/metal solution, and all solid solutions and stoichiometric compounds compatible with it, have been moved to the new FTsulf 8.2 database.
For the matte smelting system (S-Cu-Fe-Ni-Co-Pb-Zn-As), the remaining sulfide solid solutions and stoichiometric compounds are compatible with liquid matte [FTmisc-MATT]. This system has been superseded by the new FTsulf 8.2 database, which provides equally good or better results for most applications.
Complete details on FTmisc 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in Documentation.
The FTmisc databases contain data for a variety of sulfides, alloys, etc.
The databases includes dilute alloys of Fe-liquid, Pb-liquid, Sn-liquid, Cu-liquid, Cd-liquid, Te-liquid, Sb-liquid,
Se-liquid, SeTe-liquid, SbPb-liquid and PbSb-liquid each with a limited number of components, valid over limited composition ranges
In FTmisc 8.3
the MAT2 liquid sulfide/metal solution, and all solid solutions and stoichiometric compounds compatible was moved
to the new FTsulf 8.3 database.
For the matte smelting system (S-Cu-Fe-Ni-Co-Pb-Zn-As), the remaining sulfide solid solutions and stoichiometric compounds are compatible with liquid matte [FTmisc-MATT]. This system has been superseded by the new FTsulf 8.3 database, which provides equally good or better results for most applications.
In FTmisc 8.4 the liquid steel solution FTmisc-FeLq has been updated:
Complete details on FTmisc 8.4 including all the phase diagrams are given in Documentation.
FTnucl was introduced in FactSage 6.4 (2015) as a new database developed for the nuclear industry.
FTnucl contains data for pure substances and solutions containing the following elements:
Th, U, Np, Pu, Am
+ Zr, Fe, Ru, Ba + Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs
The FTnucl database can be used for the development of advanced nuclear fuels based on:
It can also be used for estimating the thermodynamic behavior and phase relationships involving fission products (based on Cs. I, Zr, Ru, Ba and Rb, and including noble gases and metallic claddings (Fe, Zr, C).
FTOxCN was introduced in FactSage 6.3 (2012)
as a new high-temperature database of Oxycarbonitride phases
that has been added to the FACT Package of Databases.
Sulfur has been added as a component to the FTOxCN database which can now be used to perform equilibrium
calculations in the Al-(Si-Ca-Mg-Fe)-C-O-N-S system at very high temperatures.
The liquid "Slag" phase is treated as a single solution phase containing all 9 elements,
valid at all temperatures and over all composition ranges of interest.
This phase thus incorporates the high-temperature oxycarbide slag, sulfide-rich liquid and
oxide slags that might appear at lower temperatures, oxynitride liquids, etc.,
all in one solution (with possible immiscibility gaps, of course).
Changes in Phase names:
Changes in phase names in FToxid :
Update to FToxid-slag for liquid FeO-TiO2-Ti2O3 solutions in better agreement with latest experimental data.
Update to FToxid for the CaO-MgO-NiO-SiO2 system including liquid, monoxide, olivine and pyroxene solutions.
The precise conditions for option 'I' phase selection are now stored within the FToxid database
- the selection of '+' or 'I' will be done for you.
Many new calculated phase diagrams have been added to the documentation for FToxid.
Changes have been made in the FToxid database to simplify the selection of phases for
calculations with the Equilib and Phase Diagram modules.
In most cases now, all solutions and all stoichiometric solid phases from FToxid visible
in the menu window can be selected.
Selection of a stoichiometric compound that is simultaneously an end-member
of a solution phase will not adversely affect the calculation.
Normally, the FactPS database should be used in combination with FToxid to select gaseous species ONLY.
Solid and liquid oxide compounds SHOULD NOT be selected from the FactPS database.
I- or J-options are introduced by default only when they are normally needed.
When there is only a small probability that an I-option or J-option is required,
it is NOT introduced by default. (This is done in order to speed up the calculation.)
However, in all solutions in which a miscibility gap could possibly occur,
this fact is mentioned in the description of that solution.
If in doubt, check.
Even though all solutions and stoichiometric compounds from the FToxid database
can now be selected in most cases, this may result in a lengthy calculation for a multicomponent system.
To speed up the calculation, one can select only those solutions that are likely to form and make all other solutions metastable. If the calculated activity of a metastable solution is > 1, this solution should be selected (made stable) and the calculation repeated.
The FToxid-SLAGG phase for C, N and CN dissolved in molten slag has been removed in FactSage 6.4.
For calculations of the solubility of C and N in molten oxides, use the FTOxCN database.
(1) Systems containing Na2O and K2O
The systems Na2O-Al2O3-CaO-SiO2 and K2O-Al2O3-SiO2 have recently been re-evaluated and re-optimized. The binary systems Na2O-X and K2O-X have been evaluated/optimized for X = Al2O3, SiO2 and TiO2, and the liquid solution is assumed ideal for X = CaO, MgO and MnO. This is intended for evaluation of the effect of Na2O and K2O on equilibria between liquid slag and iron/steel. However, only rough estimation can be made for the liquidus in multicomponent Na2O- and K2O-containing systems that are far from the optimized subsystems mentioned above.
Na was added to the melilite solid solution, which was combined with the gehlenite solid solution. This allows evaluation of the solubility of Na and B in melilite.
Several other solid solutions have been added to the database, such as nepheline, carnegeite, combeite, kalsilite, NaAlO2 and KAlO2. See detailed descriptions of these solutions by clicking on “Description of Solutions” in the documentation for FToxid.
(2) Systems containing BaO
The systems BaO-CaO, BaO-SiO2, BaO-CaO-SiO2, BaO-MnO and BaO-CaO-MnO have recently been optimized for evaluation of the effect of BaO on equilibria between liquid slag and iron/steel.
Several Ba-containing solid solutions have been added to the database, such as BaSiO3, Ba3SiO5, CaSiO3-rich pseudo-wollastonite, walstromite [Ca,Ba][Ba,Ca]CaSi3O9 and T-phase Ba2Ca(Ba,Ca)Si2O8. Ba has also been added to monoxide, wollastonite, alpha-prime Ca2SiO4 and alpha Ca2SiO4 solutions. See detailed descriptions of these solutions by clicking on “Description of Solutions” in the documentation for FToxid.
(3) Systems containing P2O5
For the system P2O5-SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-MgO-BaO-FeOx-MnO-Na2O, all binary P2O5-containing subsystems have been recently evaluated and optimized. In addition, the key subsystems CaO-MgO-P2O5, CaO-SiO2-P2O5, CaO-Al2O3-P2O5 and CaO-FeO-Fe2O3-P2O5 have been optimized and the subsystems Na2O-CaO-P2O5, Na2O-MgO-P2O5 and Na2O-SiO2-P2O5 have been approximately evaluated. This can be used for evaluation of the effect of P2O5 on equilibria among liquid slag, iron/steel and gas (solution FeLQ from the FTmisc database should be used for liquid iron/steel).
Liquidus calculations for P2O5-containing systems that substantially deviate from the optimized subsystems mentioned above may be not accurate.
(4) Oxyfluoride system Ca,Mg,Na,Al,Si//O,F
All binary, ternary and higher order subsystems of the (Ca,Na,Al,Si//O,F) and (Ca,Mg,Al,Si//O,F) systems have been optimized and the results are included into an additional slag solution, which is called FToxid-OXFL. The database can accurately calculate phase equilibria up to more than 50% of fluorides. The calculations can be less accurate when both MgO and Na2O are present in high concentrations (> 20% each). The database can be used even for fluoride systems without oxides, but it is less accurate than the FTsalt database. See detailed descriptions of FToxid-SLAG and FToxid-OXFL.
(5) Feldspar
Feldspar solution NaAlSi3O8 – KAlSi3O8 – CaAl2Si2O8 has been added to the database.
(6) Melilite
Thermodynamic properties of melilite in the following subsystems have been optimized: (Ca,Pb)2[Mg,Fe(II),Fe(III),Al,Zn]{Al,Fe(III),Si}2O7, (Ca,Na)2[Al]{Al,Si}2O7 and (Ca)2[Mg,Al,B]{Al,B,Si}2O7.
See detailed description of FToxid-Mel_ by clicking on “Description of Solutions”.
(1) CaO-MgO-NiO-SiO2 system
The CaO-MgO-NiO-SiO2 system has been reoptimized. The changes are
mostly in the Slag, Monoxide, Melilite, Clino-Pyroxene, Proto-Pyroxene
and Olivine solutions
(2) Systems containing BaO
The whole BaO-Al2O3-B2O3-CaO-MgO-SiO2 system has been optimized, including 15
solid solutions and numerous stoichiometric compounds.
(3) Na2O-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 system
The Na2O-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 system has been optimized.
The following solutions have been updated: Slag, Monoxide, Clino-pyroxene,
Mullite, Carnegieite, Nepheline, low- and high-T Meta-aluminate/ferrite
(NASl and NASh), Feldspar and beta"-alumina.
(4) Systems containing ZrO
ZrO2-containing binaries and ternaries from the
Al2O3-CaO-MgO-SiO2-ZrO2 system have been reoptimized, as well as the
MnO-ZrO2 binary. Slag, Monoxide and ZrO2-based solid solutions (cubic,
tetragonal, monoclinic) have been updated.
(5) Compound database
The FToxid compound database now includes the volumetric and thermal conductivity
parameters for 52 compounds.
(6) Minor changes
There are also a few minor updates/corrections in several solid
solutions and compounds.
Over 50 new FToxid phase diagrams have added to the 'list of stored phase diagrams'.
(1) SrO
SrO has been added to the database. The whole
SrO-BaO-Al2O3-B2O3-CaO-MgO-SiO2 system has been optimized, including 27
solid solutions and numerous stoichiometric compounds.
(2) CaO-MgO-SiO2 system
Bredigite Ca3(Ca,Mg)4Mg(SiO4)4 solid solution has been added to the
CaO-MgO-SiO2 system.
(3) Calculated phase diagrams
Approx. 50 new FToxid phase diagrams have added to the 'list of stored phase diagrams'.
There are now 421 phase diagrams (was 372 in FactSage 7.1)
including 132 (113) binary systems and 289 (259) ternary systems.
Mn2O3 has been added to the CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3-MnO system based on several optimized binary and ternary subsystems. MnO-B2O3 has also been optimized. In particular Mn3+ is added to the slag and spinel phases. 18 new stoichiometric compounds have been added to the database.
The most important binary and ternary K2O-containing systems have been optimized to add K2O to the Na2O-CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 system. 22 new stoichiometric compounds have been added to the database and a few more have been revised.
F is added to the general slag phase. Liquid oxide components can be combined now with both fluorides and sulfides. The database is most accurate when the major slag components are CaO, MgO, Na2O, Al2O3 and SiO2. The distributions of Fe and Cr between liquid metal and oxyfluoride slag are also well reproduced. Normally, the total amount of fluorides and sulfides in the slag should be kept below 50%, even though for certain subsystems the composition can extend to pure fluorides and sulfides.
The FToxid databases contain data for pure oxides and oxide solutions
of over 20 elements as well as for dilute solutions of S, SO4, PO4, H2O/OH, CO3, F, Cl and I
in the molten (slag) phase.
In FactSage 8.1 the updates to FToxid include the following changes.
Complete details on FToxid including all the phase diagrams are given in the updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
In FactSage 8.2 the updates to FToxid include the following evaluations:
In combination with the new FTsulf database,
the updated FToxid database allows calculations of Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, and As distributions between slag, liquid sulfide (matte) and liquid alloy.
Several solid solutions have been updated: Spinel (Ca and Cu added), Corundum (Ni added), Willemite (Ni added), Rhodonite (Ni added), and Monoxide.
About a dozen stoichiometric compounds containing Cu, Ni or As have been added or modified.
In addition the
Volumetric properties (density @298.15 K, thermal expansion and compressibility B')
and thermal conductivities
have been entered for the following solid oxide compounds (158 additions and modifications):
Complete details on FToxid 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in the updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
The FToxid databases contain data for pure oxides and oxide solutions
of over 20 elements as well as for dilute solutions of S, SO4, PO4, H2O/OH, CO3, F, Cl and I
in the molten (slag) phase.
FToxid 8.3
is included in the FACT 8.3 package of databases.
In FactSage 8.3 the updates to FToxid include the following:
The FToxid databases contain data for pure oxides and oxide solutions
of over 20 elements as well as for dilute solutions of S, SO4, PO4, H2O/OH, CO3, F, Cl and I
in the molten (slag) phase.
FToxid 8.4
is included in the FACT 8.4 package of databases.
In FactSage 8.4 the updates to FToxid include the following:
New compound data:-
gaseous S, S2, S3, S4, .., S8; metastable Na2SO3 and K2SO3; stable pure solid and liquid NaCl and KCl.
Temperature-dependent volumetric properties (densities) have been added in the FTsalt-SALT liquid solution for the following 50 pure liquids:
LiF, NaF, KF, RbF, CsF, MgF2, CaF2, LaF3, CeF3, LiBr, NaBr, KBr, RbBr, CsBr, MgBr2, LiI, NaI, KI, RbI, CsI, Li2CO3,
Na2CO3, K2CO3, LiNO3, NaNO3, KNO3, RbNO3, CsNO3, LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Li2SO4, Na2SO4, K2SO4, LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl,
CsCl, MgCl2, CaCl2, SrCl2, BaCl2, MnCl2, ZnCl2, PbCl2, AlCl3, LaCl3, CeCl3, CaO.
Volumetric properties (densities) have been modeled in the FTsalt-SALT liquid solution for the following 13 binary liquids:
LiF-NaF, LiF-MgF2, LiF-CaF2, NaF-MgF2, NaF-CaF2, MgF2-CaF2, NaCl-KCl, NaCl-MgCl2, NaCl-CaCl2, KCl-MgCl2, KCl-CaCl2,
MgCl2-CaCl2, CaF2-CaO.
In particular, satisfactory density calculations can be performed for the NaCl-KCl-MgCl2-CaCl2 quaternary liquid.
Note that the box 'include molar volumes' in the Equilib module must be checked in order to perform density calculations.
The FTsalt-SALT liquid solution has been extended with the addition of ZnCl2. NaCl-KCl-MgCl2-CaCl2-AlCl3-ZnCl2 is a newly
approved sub-system of FTsalt-SALT (corresponding to the ISalt-liquid solution). In particular, all five binary subsystems
involving ZnCl2 as well as the NaCl-KCl-ZnCl2 and KCl-CaCl2-ZnCl2 ternary subsystems have been optimized. The following
compounds have been added to the FTsalt pure compound database: ZnCl2(s,l), Na2ZnCl4(s), K2ZnCl4(s), KZn2Cl5(s), K5Zn4Cl13(s).
The following gaseous species have been added to the FACT53 pure compound database: ZnCl2(g), Zn2Cl4(g), NaZnCl3(g), KZnCl3(g).
The precise conditions for option 'I' phase selection are now stored within the FTsalt database
- the selection of '+' or 'I' will be done for you.
The database has been updated with 20 new solution phases and associated compounds
in the nuclear system LiF, PuF3, PuF4, ThF4,
UF3, UF4, (NiF2-CrF2-CrF3-MoF5).
The new FTsalt 7.3 database has been completely restructured, resulting in a more accurate description for many of the solid solutions.
The FTsalt databases contain data for pure salts and salt solutions of 27 main cations:
and 9 main anions:
F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, NO3, OH, CO3, SO4 as well as for dilute solutions of O2- and OH- in the molten salt phase.
In FactSage 8.0 the updates to FTsalt include the following changes.
The total number of stored FTsalt phase diagrams
is now 344 (was 338 in 7.3).
The FTsalt databases contain data for pure salts and salt solutions of 27 main cations:
and 10 main anions:
F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, NO3, ClO4, OH, CO3, SO4 as well as for dilute solutions of O2- and OH- in the molten salt phase.
In FactSage 8.1 the updates to FTsalt include the following changes.
Molten salts (52 compounds): BaBr2, BaCl2, BaF2, BaI2, BeF2, CaBr2, CaCl2, Cs2CO3, Cs2SO4, CsBr, CsCl, CsF, CsI, CsNO3, K2SO4, KBr, KCl, KF, KI, KNO2, KNO3, KOH, Li2CO3, Li2SO4, LiBr, LiCl, LiF, LiI, LiNO3, LiOH, MgCl2, MgF2, Na2CO3, Na2SO4, NaBr, NaCl, NaF, NaI, NaNO2, NaNO3, NaOH, Rb2CO3, Rb2SO4, RbBr, RbCl, RbF, RbI, RbNO3, SrBr2, SrCl2, SrF2, SrI2
Solid salts (142 phases): BaBr2, BaCaCl4, BaCl2_S1, BaCl2_S2, BaClF, BaI2, BaMgF4, BeCaF4, BeF2_S1, BeF2_S2, CaBr2, CaCl2_S1, CaCl2_S2, CaClF, CaF2_S2, Cs2BaCl4, Cs2CO3, Cs2MgCl4, Cs3MgCl5, CsBaCl3, CsBr_S1, CsBr_S2, CsCaCl3, CsCl_S1, CsCl_S2, CsF, CsI_S1, CsI_S2, CsMgCl3, CsMg3Cl7, CsNO3_S1, CsNO3_S2, CsSrCl3, K2BaCl4, K2ClNO3, K2CO3_S1, K2CO3_S2, K2MgCl4, K2MgF4, K2SO4_S1, K2SO4_S2, K2SrCl4, K3FCO3, K3F(SO4)_S1, K3F(SO4)_S2, K3Mg2Cl7, KBr_S1, KBr_S2, KCaCl3_S1, KCaCl3_S2, KCaCl3_S3, KCaF3_S1, KCaF3_S2, KCl_S1, KCl_S2, KF, KI_S1, KI_S2, KMgCl3_S1, KMgCl3_S2, KMgF3, KNO2_S1, KNO2_S2, KNO3_S1, KNO3_S2, KOH_S1, KOH_S2, KSr2Cl5, Li16BaSrF20, Li2CO3_S1, Li2CO3_S2, Li2CO3_S3, Li2SO4, LiBaF3, LiBr, LiCl, LiCs2Cl3, LiCsBr2, LiCsF2, LiF, LiI, LiKMgCl4, LiNO3, LiOH, LiRbBr2, LiRbCl2, LiRbF2, LiRbI2, MgBa2Cl6, MgCl2, MgF2, Na2CO3_S1, Na2CO3_S2, Na2CO3_S3, Na2MgCl4, Na2SO4_S1, Na2SO4_S2, Na2SO4_S3, Na2SO4_S4, Na3F(SO4), Na3Mg2BaCl9, NaBr, NaCl, NaF, NaI, NaMgCl3, NaMgF3_ S1, NaMgF3_ S2, NaNO2_S1, NaNO2_S2, NaNO3_S1, NaNO3_S2, NaOH_S1, NaOH_S2, Rb2BaCl4, Rb2CO3_S1, Rb2CO3_S2, Rb2MgCl4, RbBr_S1, RbBr_S2, RbCaCl3, RbCl_S1, RbCl_S2, RbF, RbI_S1, RbI_S2, RbMgCl3, RbNO3_S1, RbNO3_S2, RbNO3_S3, RbNO3_S4, RbSr2Cl5, RbSrCl3, SrBr2_S1, SrBr2_S2, SrCl2_S1, SrCl2_S2, SrClF, SrF2, SrI2, SrMgF4_S1, SrMgF4_S2
The total number of stored FTsalt phase diagrams
is now 351 (was 344 in 8.0).
Complete details on FTsalt including all the phase diagrams are given in Documentation
in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
The FTsalt databases contain data for pure salts and salt solutions of 27 main cations:
and 10 main anions:
F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, NO3, ClO4, OH, CO3, SO4 as well as for dilute solutions of O2- and OH- in the molten salt phase.
In FTsalt
volumetric properties (density @298.15 K, thermal expansion and compressibility B')
and thermal conductivities
have been entered for the following compounds and solutions (99 additions and modifications):
Solid salts (94 phases)
Liquid salts (5 phases)
Four new compounds LiClO4, LiNO2, KLi(NO3)2 and KLi3(NO2)4 have been added to the compound database
and three compounds LiNO3, Li2CO3 and KLiCO3 have been updated.
LiClO4 has been added to the PERC solid solution,
and two new LiNO2-rich solid solutions (LiNA and LiNB) have been introduced.
The SALTK liquid solution permits calculations for nitrate-rich solutions.
The reciprocal ternary sub-systems
Na, Li // NO3, NO2; K, Li // NO3, NO2; Na, Li // NO3, Cl; K, Li // NO3, Cl; Na, Li // NO3, CO3; K, Li // NO3, CO3; Na, Li // NO3, ClO4 and K, Li // NO3, ClO4
have been newly evaluated and optimized at all compositions (including all binary common-ion sub-systems), based on the experimental data available in the literature.
This includes updates for the K2CO3-Li2CO3, KNO3-LiNO3, Li2CO3-LiCl, Li2CO3-LiNO3, Li2CO3-Na2CO3, LiCl-LiNO3 and LiNO3-NaNO3 binary sub-systems.
In SALTK, LiX-NaX, LiX-KX and NaX-KX (where X = NO2, Cl, CO3 or ClO4) as well as LiCl-Li2CO3, NaCl-Na2CO3 and KCl-K2CO3
(which were already available in SALTF) are the only solute-solute binary common-ion sub-systems that have been optimized.
Note that reactions of the type 4 ANO2 + BClO4 = 4 ANO3 + BCl (where A, B = Li, Na or K) have a very negative Gibbs energy change and thus are strongly shifted to the right. In order to inhibit those reactions (which may be kinetically hindered), it is possible to use virtual elements (This new feature was introduced in FactSage 8.1). Some detailed examples are provided in the Equilib Advanced Slide Show (see in particular example 15.6).
The total number of stored FTsalt phase diagrams
is now 367 (was 351 in 8.1).
Complete details on FTsalt 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
The FTsalt databases contain data for pure salts and salt solutions of 27 main cations:
and 10 main anions:
F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, NO3, ClO4, OH, CO3, SO4 as well as for dilute solutions of O2- and OH- in the molten salt phase.
In the compound FTsalt database new compounds
Mg(NO3)2, Mg(NO2)2, Mg(ClO4)2(s1,s2,s3), K2Mg(CO3)2 and K2Mg(NO3)4(s1,s2)
have been added and existing compounds
MgCO3, CeCl3, Na3Ce5Cl18, K2CeCl5, K3CeCl6, K3Ce5Cl18, RbCe2Cl7, Rb2CeCl5, Rb3CeCl6, CsCe2Cl7 and Cs3CeCl6
have been modified.
In the solution FTsalt database new liquid solutions
SALTL (K, Mg // NO3, NO2, Cl, CO3, ClO4) and SALTM (Li, Na, K, Mg, Ca, Ce // Cl) have been added.
In addition three new CeCl3-based solid solutions have been introduced :
(K,Na)3CeCl6(ss), (K,Na)2CeCl5(ss) and
(K,Na)3Ce5Cl18(ss) (with the nicknames A3C1, A2C1 and A3C5, respectively).
The SALTL liquid solution permits calculations for KNO3-rich solutions
with MgCO3 or MgX2 contents up to about 5 wt% (where X = NO2, Cl or ClO4).
Owing to the lack of phase diagram data, the common-ion binary sub-systems
K2CO3-MgCO3, Mg(NO3)2-MgCO3, KNO2-Mg(NO2)2, Mg(NO3)2-Mg(NO2)2, MgCl2-Mg(NO3)2, KClO4-Mg(ClO4)2 and Mg(NO3)2-Mg(ClO4)2
were estimated based on chemically similar systems.
For nitrate-rich solutions without Mg solutes,
the SALTK liquid solution (currently Li, Na, K // NO3, NO2, Cl, CO3, ClO4) can be used.
The SALTM liquid solution permits calculations for CeCl3-containing solutions
with Mg and/or Ca, but without Rb and Cs.
The ternary sub-systems LiCl-MgCl2-CeCl3, KCl-MgCl2-CeCl3, LiCl-CaCl2-CeCl3, NaCl-CaCl2-CeCl3 and MgCl2-CaCl2-CeCl3
have been newly evaluated and optimized at all compositions, while the ternary sub-systems
LiCl-KCl-CeCl3 and NaCl-KCl-CeCl3 have been substantially improved.
For CeCl3-containing solutions with RbCl and/or CsCl,
the SALTG liquid solution (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, La, Ce // Cl) can be used
The total number of stored FTsalt phase diagrams
is now 377 (was 367 in 8.2).
FTsalt 8.3
is included in the FACT 8.3 package of databases.
Complete details on FTsalt 8.3 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
The FTsalt databases contain data for pure salts and salt solutions of 29 main cations:
and 15 main anions:
F, Cl, Br, I, NO2, NO3, ClO4, OH, CO3, SO4,
S2O7, CrO4, Cr2O7, MoO4, Mo2O7
as well as for dilute solutions of O2- and OH- in the molten salt phase.
In FactSage 8.4 the updates to FTsalt include the following
Also, compressibility expressions
(as a function of temperature) have been modified for the following pure liquid salts:
LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, CsCl, MgCl2, CaCl2, SrCl2, BaCl2, LiF, NaF, KF, RbF, CsF, MgF2,
CaF2, LiBr, NaBr, KBr, RbBr, CsBr, MgBr2, LiI, NaI, KI, RbI, CsI, Li2CO3, Na2CO3, K2CO3,
LiNO3, NaNO3, KNO3, RbNO3, CsNO3, Li2SO4, Na2SO4, K2SO4, LiOH, NaOH, and KOH.
In the solution FTsalt database new liquid solutions SALTN
(Na, K // Cl, CO3, SO4, S2O7, CrO4, Cr2O7, MoO4, Mo2O7, O - diluted in oxides),
SALTO (Na, K, Zn, Pb // Cl) and SALTP (Na, K, Hg, Hg2 // Cl) have been added.
In the case of SALTN, the model for the Na, K // Cl, CO3, SO4, S2O7 sub-system
is identical to that in the FTpulp database.
In addition seven new solid solutions have been introduced :
one pyrosulfate solid solution (KPyr), one pyrosulfate/dichromate solid solution
(Na2S2O7), two dichromate/dimolybdate solid solutions (K2Cr2O7 and Na2Cr2O7),
and three molybdate/chromate/sulfate solid solutions (K2MoO4(s3), Na2MoO4(s1)
and Na2MoO4(s2)).
Several solid solutions have been extended :
addition of the CrO4[2-] and MoO4[2-] anions to the solid solutions Dbeta-K2SO4,
alpha-K2SO4, Glaserite, and Na2SO4-V; addition of the CO3[2-] and MoO4[2-] anions
to the Na2CrO4 solid solution; and addition of the SO4[2-] anion to the solid
solutions gamma-Na2CO3 and beta-Na2CO3.
The SALTN (Na, K // Cl, CO3, SO4, S2O7, CrO4, Cr2O7, MoO4, Mo2O7,
O - diluted in oxides) liquid solution is the only FTsalt molten salt solution
containing A2MO4 and / or A2M2O7 (with A = Na, K and M = Cr, Mo).
The SALTO (Na, K, Zn, Pb // Cl) liquid solution is the only FTsalt molten
salt solution containing both ZnCl2 and PbCl2.
The SALTP (Na, K, Hg, Hg2 // Cl) liquid solution is the only FTsalt molten salt solution containing HgCl2.
The total number of stored FTsalt phase diagrams
is now 419 (was 377 in 8.3).
FTsalt 8.4
is included in the FACT 8.4 package of databases.
Complete details on FTsalt 8.4 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
The new FTsulf databases
contain solutions and stoichiometric compounds in the Cu-Fe-Ni-Co-Cr-Mn-Pb-Zn-As-O-S
system evaluated/optimized by the FACT group for applications involving equilibria among metal, liquid and solid sulfide phases, liquid and solid oxide phases and gas.
This includes pyrometallurgy, hot corrosion, etc. The FTsulf solution database
contains sulfide solutions and three major metal solutions (liquid, bcc and fcc), which are compatible with the sulfide solutions.
The FTsulf compound database contains
all stoichiometric sulfide, sulfate and arsenide compounds evaluated/optimized by the FACT group to be thermodynamically consistent with the FTsulf solution database.
For nearly all calculations involving sulfide solutions, the FTsulf databases
supersede the FTmisc databases.
In particular for calculations involving matte smelting, the FTsulf databases
will provide better results in nearly all cases due to many improvements to the optimizations
[2135-2139, 4023-4028, 4031-4035].
For example, the MAT2 phase is now more consistent with the FToxid
and FSstel databases, contains oxygen as a component,
and can be used at all compositions from pure metal to pure sulfide.
Complete details on FTsulf 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in the updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
In FactSage 6.3 the phase selection has been simplified by introducing specific modifications in
the FScopp database files.
These modifications are new to FScopp and are intended to simplify automatic species and phase selection.
The selection of certain solution phases now automatically assigns two-phase immiscibility (I-option)
in those cases where this is deemed appropriate.
Furthermore, certain solution phases will not be shown on the menu pages of the
Equilib or Phase Diagram modules, and hence cannot be selected, if components
essential to that phase are missing in the input reactants.
Consequently, with FactSage 6.3, loading a private Phas*.dat or Equi*.dat file,
stored previously using an earlier version of FactSage, and containing a now restricted
phase, may result in the message "The following solution phase could not be located ..." being generated.
In such cases, calculations can still be made as before since the restricted phase is not stable
in any case as shown from previous calculations.
In the new solution database, one or two solution phase names have been changed.
If, upon loading a private Phas*.dat or Equi*.dat file, stored previously using an earlier
version of FactSage, the message "The following solution phase could not be located ..."
appears, and if it is known from previous calculations that the missing phase is actually stable,
then reference to the phase diagram stored in the documentation will permit the new phase
name to be determined.
FScopp 7.3 is a major update of the FactSage Copper Alloy Database.
Elements Ba+Sr+Ce+Nd+Pr+Sm+Y have been removed from the old database and H+Hg+W have been added.
The elements removed were not commonly found in Cu alloys, whereas the ones added are more important for Cu alloys and their treatments.
The new FScopp 7.3 database now contains 40 elements:
In the old database there were 37 fully assessed binary systems and 134 partially assessed binary systems for a total
of 171 binary systems.
In the new FScopp 7.3 database,
there are now 322 fully assessed binary systems and 89 partially assessed binary systems for a total of 411 binary systems.
The assessed binary systems are now fully in agreement with their respective systems in the
FSlead 7.3 and FTlite 7.3 databases (7.3).
A spreadsheet listing all the FScopp 7.3 binary assessments has been prepared that
summarises the quality of the evaluations (top, good or poor).
The spreadsheet is new in FactSage 7.3 and is accessible via the Documentation module and
View Data module - for details see SpMCBN below.
More than a third of the assessed systems have the modeling of the Gibbs energy of their liquid phase represented by the Modified Quasichemical Model in the Pair Approximation (MQMPA) which takes into account the short-range-order between species (i.e. Cu-Fe-S, Ag-Te, etc.), while the older database simply used a Bragg-Williams approach (i.e. random mixing).
This is a major upgrade of the database.
Minor update: - there is a correction to the volumetric properties of the Ag(fcc) pure substance
in the compound database (s1) and to the FCC_A1 phase in the solution database.
FScopp is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Cu alloys.
Several dozen ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also been evaluated.
Complete details on FScopp 8.2 including all the phase diagrams
are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FScopp is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Cu alloys.
In addition, several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also
been evaluated.
The FScopp 8.3 database contains 269 solution phases (238 in 8.2) and 1077 pure compounds (906 in
8.2) with 1442 stoichiometric phases (1232 in 8.2) counting allotropic forms.
Complete details on FScopp 8.3 including all the phase diagrams
are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FScopp is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Cu alloys.
In addition, several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also
been evaluated.
The FScopp 8.4 database contains 330 solution phases (269 in 8.3) and 1471 pure compounds
(1077 in 8.3) with 1891 stoichiometric phases (1442 in 8.3) counting allotropic forms.
Complete details on FScopp 8.4 including all the phase diagrams
are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FSlead 7.3 is a major update of the FactSage Lead Alloy Database.
Elements Al+Ge+Mn+Pd+Si+Zr have been removed from the old database and Ba+H have been added.
The new FSlead 7.3 database now contains 25 elements:
In the old database there were 26 fully assessed binary systems and 31 partially assessed binary systems for a total of 57 binary systems.
In the new FSlead database, there are 161 fully assessed binary systems .
The assessed binary systems are now fully in agreement with their respective systems in the FScopp 7.3
and FTlite 7.3 databases.
A spreadsheet listing all the FSlead 7.3 binary assessments has been prepared that
summarises the quality of the evaluations (top, good or poor).
The spreadsheet is new in FactSage 7.3 and is accessible via the Documentation module and
View Data module - for details see SpMCBN below.
More than a third of the assessed systems have the modeling of the Gibbs energy of their liquid phase represented by the Modified Quasichemical Model in the Pair Approximation (MQMPA) which takes into account the short-range-order between species (i.e. Pb-Zn-S, Ag-Te, etc.), while the older database simply used a Bragg-Williams approach (i.e. random mixing).
This is a major upgrade of the database.
Minor update: - there is a correction to the volumetric properties of the Ag(fcc) pure substance
in the compound database (s1) and to the FCC_A1 phase in the solution database.
FSlead
is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Pb alloys.
Several dozen ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also been evaluated.
Complete details on FSlead 8.2
including all the phase diagrams are given in
'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FSlead
is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Pb alloys.
In FSlead 8.3 a total of 235 binary systems (223 in 8.2) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is shown here for the major and minor alloying elements of Pb-alloys.
In addition, several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also been evaluated.
Complete details on FSlead 8.3
including all the phase diagrams are given in
'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FSlead
is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving Pb alloys.
In FSlead 8.4 (27 elements) a total of 238 binary systems (235 in 8.3) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is shown here for the major and minor alloying elements of Pb-alloys.
In addition, several dozens of ternary systems have been assessed, and important quaternary systems have also been evaluated.
The FSlead 8.4 database contains 127 solution phases (125 in 8.3) and 434 pure compounds (415 in 8.3) with 641 stoichiometric phases (618 in 8.3) counting allotropic forms.
Complete details on FSlead 8.4
including all the phase diagrams are given in
'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
Species selection with the Equilib and Phase Diagram modules has been made simpler. (Try it and see.)
Some minor updates. Compound MoS2(s2) removed.
Changes in phase names in FSstel :
Amendments and updates have been made to 10 binary sub-systems:
Al-Mn, Al-N, Al-Zn, C-Mn, C-Mo, Co-Si. Cr-N, Cu-Zn, Fe-Nb, Hf-Mo.
The amendments provide improved descriptions and calculations for steels involving the elements listed.
The database has been updated to incorporate new assessed data for the following binary systems:
C-Zr, Hf-Nb, Hf-V, Hf-W, Hf-Zr, Nb-Ta, Ta-V, Ta-Zr, Ti-Zr, V-W, V-Zr, W-Zr
and for the following ternary and quaternary systems:
Al-C-Fe, Al-C-Mn, Al-C-Fe-Mn, C-Hf-Nb, C-Hf-W, C-Nb-Ta, C-Nb-Ti, C-Nb-V, C-Nb-W, C-Nb-Zr, C-Ta-W, C-Ti-W, C-V-W, C-W-Zr.
Parameters for the Cd-Pb system have been revised.
In FactSage 6.3 phase selection has been simplified by introducing specific modifications in
the FSstel database files.
These modifications are new to FSstel and are intended to simplify automatic species and phase selection.
The selection of certain solution phases now automatically assigns two-phase immiscibility (I-option)
in those cases where this is deemed appropriate.
Furthermore, certain solution phases will not be shown on the menu pages of the
Equilib or Phase Diagram modules, and hence cannot be selected, if components
essential to that phase are missing in the input reactants.
Consequently, with FactSage 6.3, loading a private Phas*.dat or Equi*.dat file,
stored previously using an earlier version of FactSage, and containing a now restricted
phase, may result in the message "The following solution phase could not be located ..." being generated.
In such cases, calculations can still be made as before since the restricted phase is not stable
in any case as shown from previous calculations.
In the new solution database, one or two solution phase names have been changed.
If, upon loading a private Phas*.dat or Equi*.dat file, stored previously using an earlier
version of FactSage, the message "The following solution phase could not be located ..."
appears, and if it is known from previous calculations that the missing phase is actually stable,
then reference to the phase diagram stored in the documentation will permit the new phase
name to be determined.
The FSstel database has been modified to simplify the selection of species
when the Equilib or Phase Diagram modules are being used.
Phases that are not possibly relevant to the calculation at hand will not appear in the menu window.
Furthermore, if one now simply selects all the solution phases from FSstel and all the pure solid phases
from FSstel that appear in the menu window, a correct calculation will result in most cases,
with the I- or J-option (for possible immiscibility) automatically selected if possibly required.
The FSstel database has been updated and recently assessed data relating to galvanizing processes associated with the Fe-Al-Mg-Mn-Zn system have been incorporated.
These include revised data for the Fe-Zn system and parameters allowing representation of the likely influence of small concentrations of Mg and Mn on previously calculated ternary phase equilibria.
In addition, the assessed parameters reported by Danielsen and Hald (Calphad 31 (2007) 505) for the Z-phase,
found in new 8-12% Cr martensitic steels, have been converted to FactSage format and incorporated in the present database.
Individual systems for which parameters have been updated or newly included are:
C-Mn, Fe-Si, Mo-Ti, N-Si, Ni-Si
C-Cr-Fe, C-Cr-Mn, C-Cr-Si, C-Cr-Ti, C-Fe-Mn, C-Fe-W, C-Mn-Si, C-Mn-V, C-Mo-Ti, C-Mo-V, C-N-Ti, C-Ni-Si, C-Ni-Ti, C-Ni-W, C-V-W, Cr-Fe-Mn, Cr-Fe-W, Cr-Mn-N, Cr-Mn-Ni, Cr-Mn-Ti, Cr-Mo-N, Cr-N-N, Cr-N-W, Fe-Mn-N, Fe-Mn-Ni, Fe-Ni-Si, Fe-Ni-Ti, Mn-Ni-V, N-Si-Ti
C-Cr-Fe-Mn, C-Cr-Fe-W, C-Cr-Mo-V, Cr-Fe-Mn-N
- Revision of the description of the Fe-Si-C system.
The description of The Fe-Mn-Si-Al-C system for AHSS calculation is improved.
- Revision of the Fe-Ti-C system.
Better description of TiC formation.
- Revision of the Al-Fe-Zn system.
Inconsistency of Al-Fe-Zn system for Zn galvanizing calculation is resolved.
FSstel 7.3 is a major update of the FactSage Steel Alloy Database.
The FSstel 7.3 database contains 31 elements:
The number of optimized binary systems has been increased to 205 systems (was 140 in 7.2).
Many ternary and high order systems have been re-optimized and new systems optimized.
The number of stoichiometric compounds has been increased to 437 phases (was 306 in 7.2).
The liquid phase is now described by the Modified Quasichemical Model (MQM).
Within this model, many previous optimizations by random mixing model and new optimizations by MQM
have been integrated to give more accurate description of the liquid solution in binary, ternary and higher order systems.
The deoxidation and desulfurization behavior of liquid steel are well described in this model.
For the accurate description of deoxidation of Fe-Ca and Fe-Mg liquid solution, CaO and MgO associate species have been incorporated into the liquid phase.
The following systems have been completely re-assessed to reproduce recent experimental data for high alloyed steels and other steel systems:
FSstel covers a wide range of commercial grade carbon steels and stainless steels, and new high advanced steels under development.
With the addition of hydrogen (H) the database now contains 32 elements:
In FactSage 8.0 the FSstel database now includes
With hydrogen (H) now included in the database, the hydrogen solubilities in liquid and solid FCC, BCC, HCP, etc. are well represented.
The updates for P and N-containing systems are done as a continuation from FSstel 7.3.
The model parameters for 18 new binary systems and 10 new ternary systems, as well as several quaternary system, are now included.
In summary, the following systems have been updated:
The total number of stored FSstel phase diagrams
is now 221 (was 198 in 7.3).
FSstel covers a wide range of commercial grade carbon steels and stainless steels, and new high advanced steels under development.
With the addition of hydrogen (H) in FactSage 8.0 the database contains 32 elements:
This includes 22 new binary and 41 ternary systems, and 25 new solution phases and 38 new compounds.
The total number of stored FSstel phase diagrams
is now 304 (was 221 in 8.0).
Complete details on FSstel 8.1 including all the phase diagrams are given in 'Documentation'
in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
With the addition or update of 16 rare earth elements (RE) the FactSage 8.2 database now contains 46 elements (was 32 in FactSage 8.1):
The database related to Nd magnet (Fe-Nd-B-Dy-Pr-Tb) and its recycling process using liquid metal has been updated.
The updates include 87 new binary, 7 updated binary, 10 new ternary and several new quaternary and high order systems.
11 new solution phases and 452 new compounds have also be added.
The total number of stored FSstel phase diagrams
is now 307 (was 304 in 8.1).
Complete details on FSstel 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FSstel covers a wide range of commercial grade carbon steels and stainless steels, and new high advanced steels under development.
The FactSage 8.3 database contains 46 elements (was 32 in FactSage 8.1):
The FactSage FSstel steel database is based on relevant steel sub-systems from the
old SGTE Solution database, but now incorporates updates of those systems as well as new published assessments.
“Tramp elements” have also been included to allow calculations relating to recycling and removal of unwanted impurities to be performed.
In this update, numerous binary Cr-RE (RE = Rare Earth elements) system were newly added
as part of our continue effort to put RE in steel database.
Many binary systems containing Ca, Mg, Nb and Zn were newly added
or updated for more accurate chemical reaction calculations
in the refining process of super alloys and Zn galvanizing process of high alloyed steels.
Binary systems containing Sc were also largely updated.
These include 47 new binary systems, and several new ternary systems.
2 new solution phases and 57 new compounds are included in 8.3 version.
In summary, in FSstel the following systems have been added or updated.
The total number of stored FSstel phase diagrams
is now 352 (was 307 in 8.2).
Complete details on FSstel 8.3 including all the phase diagrams are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
FSstel covers a wide range of commercial grade carbon steels and stainless steels, and new high advanced steels under development.
The FactSage 8.4 database contains 46 elements:
The FactSage FSstel steel database is based on relevant steel sub-systems from the
old SGTE Solution database, but now incorporates updates of those systems as well as new published assessments.
"Tramp elements" have also been included to allow calculations relating to recycling and removal of unwanted impurities to be performed.
FSstel contains 381 completely assessed 61 partially assessed binary alloy systems,
together with approximately 168 ternary and 29 quaternary systems for which assessed parameters are available for phases of practical relevance.
It contains 181 solution phases and 1015 stoichiometric compounds.
In FSstel the following systems have been added or updated.
(1) Updates
Update of Mu_phase and Sigma phase for binary and ternary systems
Mu_phase and Sigma phase form extensive solid solutions in the Fe-Co-Cr-Mn-Mo-Nb-Ni-Ta system,
which is important for high entropy alloys, and Ni- and Co-super alloy systems.
Mu_phase and Sigma phase in binary and ternary systems were updated for better description of phase diagrams.
In several ternary systems, FCC, BCC, liquid and other solutions were also updated simultaneously.
Co-Mo system: change of Mu_phase, Sigma phase, liquid phase
(b) Ternary systems
Co-Fe-Mo system: update of Mu_phase, Sigma, FCC, Liquid
(2) Hydrogen containing systems (Hydrogen solubility in V-rich BCC phase)
(3) FCC L12 and BCC B2 order phase
(4) Minor updates:
The total number of stored FSstel phase diagrams
is now *** (was 352 in 8.3).
Complete details on FSstel 8.4 including all the phase diagrams are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
SGTE(2007) database was introduced in FactSage 6.1 (2009)
as a major expansion and update of the previous SGTE(2004) alloy database
with many more fully assessed systems.
As well, many previous assessments have
been re-evaluated and re-optimized based upon recent data.
SGTE(2011) database was introduced in FactSage 6.4 (2013)
as an update of the previous SGTE(2007)
In FactSage 6.4, the SGTE(2011) database has been modified to simplify the selection of species when the
Equilib or Phase Diagram modules are being used.
Phases that are not possibly relevant to the calculation at hand will not appear in the menu window.
Furthermore, if one now simply selects all the solution phases from SGTE(2011) and all the pure solid phases
from SGTE(2011) that appear in the menu window, a correct calculation will result in most cases,
with the I- or J-option (for possible immiscibility) automatically selected if possibly required.
BINS - the SGTE free binary alloy database -
has been updated to be consistent with the new SGTE(2014) database.
The SGTE(2014) database represents a significant update and revision of the previous SGTE(2011) alloy database.
The 78 elements included in the database are:
From among these elements, there are some 577 completely assessed binary alloy systems, of which over 32 are newly assessed systems and many others have been revised or amended on the basis of newly published experimental information. The database also includes about 141 ternary and 15 higher-order systems for which assessed parameters are available for phases of practical relevance. The systems now incorporate approximately 317 different solution phases and 1166 stoichiometric intermetallic compound phases.
This version of the SGTE Solution Database thus represents a significantly upgraded general alloy database. The database is intended to provide a sound basis for calculations relating to the production, heat treatment, constitution, and application of a wide range of alloy types.
BINS - the SGTE free binary alloy database -
has been updated to be consistent with the new SGTE(2017) database.
The SGTE(2017) database represents a significant update and revision of the previous SGTE(2014) alloy database.
The 79 elements included in the database are,
From among these elements, there are some 603 completely assessed binary alloy systems,
of which 15 are newly assessed systems and
28 others have been revised or amended on the basis of newly published experimental information.
The database also includes about 141 ternary and 20 higher-order systems for which assessed
parameters are available for phases of practical relevance.
The systems now incorporate 318 different solution phases and 1227 compound phases
(mainly stoichiometric intermetallics).
Complete details on SGTE(2017) are given in 'Documentation'
in the FactSage Main Menu.
The SGTE(2020) database represents a significant update and revision of the previous SGTE(2017) alloy database.
The 79 elements included in the database are,
From among these elements, there are some 690 completely assessed binary alloy systems,
of which 92 are newly assessed systems and
many others have been revised or amended on the basis of newly published experimental information.
The database also includes about 141 ternary and 15 higher-order systems for which assessed
parameters are available for phases of practical relevance.
The systems now incorporate approximately 365 different solution phases and 1470 compound phases
(mainly stoichiometric intermetallics).
The total number of stored SGTE(2020) phase diagrams is 1299
(cf. 1176 in SGTE(2017))
Complete details on SGTE(2020) including all the phase diagrams are given in Documentation
in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
Minor correction - the selection of SGTE(2020) compounds
(pure substances) as possible products has been corrected in 27 pre-calculated phase diagrams
The SGTE(2022) database is new and represents a significant update and revision of the previous
SGTE(2020) alloy database.
The 79 elements included in the database are,
100 new binary systems and 1 ternary system have been added and 17 systems have been updated.
Complete details on SGTE(2022) with revised documentation and all the calculated
phase diagrams are given in Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
The SGTE(2024) database is new and represents a significant update and revision of the previous
SGTE(2022) alloy database.
The 79 elements included in the database are
96 binary systems and 12 ternary system have been added, and updates have been applied to 19 binary systems.
THe total number of phase diagrams is now 1363.
Complete details on SGTE(2024) with revised documentation and all the calculated
phase diagrams are given in Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
SGnobl was introduced in FactSage 6.1 (2009)
as a major expansion and update of the previous FSnobl database for noble
metal alloys. The number of fully assessed binary and ternary systems has
nearly doubled and many previous assessments have been re-evaluated and
re-optimized based upon recent data.
The number of binary and ternary systems compared with the previous version of the database is 204 (130) and 122 (7) respectively.
While
experimental data from original publications have been used in many cases, the large increase in system content
is due, in large part, to the use of three major sources of information, namely
Handbook of Ternary Alloy Phase Diagrams, eds. P. Villars, A. Prince, H. Okamoto, ASM, 1997.
Ternary Alloys, eds. G. Petzow, G. Effenberg, VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, Vols.1-3, (1988,1990).
The calculation model for enthalpies of formation, due to X.-Q. Chen and R. Podloucky
(CALPHAD 30 (2006) 266-269), which is based on a revised Miedema method in combination with ab initio results.
Use of these resources has enabled the general scarcity of experimental thermodynamic information for many noble
metal systems to be compensated, while retaining a reasonable level of reliability of the resulting assessments.
In addition, the database has been updated and made compatible with assessments for noble metal-containing systems, originating from work carried out within the framework of COST Action 531, Lead-Free Solders.
(Atlas of Phase Diagrams for Lead-Free Soldering compiled by A.T. Dinsdale, A.Watson, A. Kroupa,
J. Vrestal, A. Zemanova, and J. Vizdal, published in 2008 by the European Science Foundation)
Many minor improvements have been made including:
- Si in the solution phase DIAMOND_A4 now has the same stability as in Si(s)(diamond_a4)
There is an important major improvement:
- the calculated phase diagram no longer depends on the inclusion/exclusion of the pure elements in the phase selection.
Calculation with both solution phases and pure elements selected leads to the same result as calculating with only the solution phases selected.
A spreadsheet listing all the SGnobl 7.3 binary assessments has been prepared.
The spreadsheet is new in FactSage 7.3 and is accessible via the Documentation module and
View Data module - for details see SpMCBN below.
This is a new database from SGTE for alloy systems involving the following elements
which are components of lead-containing and lead-free solders: Ag, Au, Bi, Cu, In, Ni,
Pb, Pd, Sb, Sn, Zn.
The documentation has been revised and new diagrams have been added.
The new phase diagrams include 20 ternary systems and a large number of special isothermal sections
for which assessed parameters are available for phases of practical relevance.
The total number of stored phase diagrams is now 164 (was 55).
SpMCBN was introduced in FactSage 6.4 (2015) as a new database that contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys include
Me1-Me2-C, Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si and Me-B-Si systems.
The database is compatible with assessed data for relevant binary, and some ternary systems from the SGTE2011 Solution Database, but the SpMCBN Database incorporates thermodynamic parameters for very many previously un-assessed systems. Calculations of thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams can be carried out for approximately 180 binary, and over 200 ternary systems, for the individual temperatures or temperature ranges covered by the available experimental information.
The general procedure used in obtaining assessed parameters for the solution and compound phases of the large number of previously un-assessed ternary systems in the SpMCBN Database has been to combine the phase boundary information contained in the ASM Handbook of Ternary Alloy Phase Diagrams with available assessed thermodynamic data for the appropriate binary sub-systems. This has allowed a completely compatible set of values to be derived to describe binary and ternary thermodynamic properties and phase equilibria for a particular system.
The elements included in the Spencer Group SpMCBN refractory database are:
B, C, N, Si with
Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Fe, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Re, Sc, Ta, Tc, Ti, V, W, Y, Zr
Approx. 180 new SpMCBN phase diagrams have optimized and added to the 'list of stored phase diagrams' bringing the total to 633.
(1) Amended systems
B-Fe B-Si Hf-N
(2) New binary systems
B-Re B-Tc B-Y C-Re C-Sc C-Tc Co-Hf Co-Sc Co-Ti Cr-Hf Cr-Re Cr-Sc Cr-Y
Fe-Hf Hf-Re Hf-Y Mo-Re Mo-Sc Mo-Tc Mo-Y N-Y Nb-Re Nb-Sc Nb-Y Ni-Re Ni-Sc Ni-Tc
Re-Sc Re-Si Re-Tc Re-Ti Re-V Re-Y Re-Zr Sc-Si Sc-Ta Sc-Ti Sc-W Ta-Y
Tc-Ti Tc-W Ti-Y V-Y W-Y
(3) New ternary systems
Al-B-C Al-B-Co Al-B-Cr Al-B-Fe Al-B-Mo Al-B-N Al-B-Nb Al-B-Ni
Al-B-Re Al-B-Ti Al-B-V Al-B-Zr Al-C-Co Al-C-Cr Al-C-Fe Al-C-Hf
Al-C-Mo Al-C-Nb Al-C-Ni Al-C-Sc Al-C-Ta Al-C-Ti Al-C-V Al-C-W
Al-C-Zr Al-Cr-N Al-Hf-N Al-Mo-N Al-N-Nb Al-N-Ni Al-N-Si Al-N-Ta
Al-N-Ti Al-N-V Al-N-W Al-N-Zr
SpMCBN contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys include Me1-Me2-C,
Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si and Me-B-Si systems.
The database has been updated and new ternary refractory metal Me1-Me2-Me3 systems have also been added.
The lists of the new and revised binary and ternary systems are as follows:
The spreadsheet is new in FactSage 7.3 and is accessible via the Documentation module:
It is also available in the View Data module:
SpMCBN contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys comprise the following systems:
The elements included in SpMCBN are:
Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Fe, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Re, Sc, Ta, Tc, Ti, V, W, Y, Zr
In FactSage 8.0 the database has been updated and new binary and ternary systems have been added.
The lists of the new and revised binary and ternary systems are as follows:
A spreadsheet listing all the SpMCBN 8.0 binary assessments has been prepared that
summarises the quality of the evaluations (top, good or poor).
The spreadsheet is accessible via the Documentation module:
It is also available in the View Data module:
Co-Cr-Fe, Co-Cr-Mo, Co-Cr-Ni, Co-Cr-Ta, Co-Cr-Zr, Co-Fe-Mn, Co-Fe-Mo,
Co-Fe-Nb, Co-Fe-Ni, Co-Fe-Ti, Co-Fe-Y, Co-Fe-Zr, Co-Mo-Ni, Co-Mo-W,
Co-Mo-Zr, Co-Nb-Ta, Co-Nb-W, Co-Ni-Re, Co-Ni-Ta, Co-Ni-Ti, Co-Ni-Y,
Co-Re-Y, Co-Ti-V, Co-Ti-Zr
Cr-Fe-Mn, Cr-Fe-Nb, Cr-Fe-Ti, Cr-Fe-Y, Cr-Fe-Zr, Cr-Hf-Ni, Cr-Hf-V, Cr-Hf-Zr,
Cr-Nb-Ni, Cr-Nb-V, Cr-Nb-W, Cr-Ni-Sc, Cr-Re-Ta, Cr-Re-W, Cr-Ti-V,
Cr-V-Zr, Cr-W-Zr
Fe-Hf-Y, Fe-Hf-Zr, Fe-Mo-Nb, Fe-Mo-Ta, Fe-Mo-Ti, Fe-Mo-V, Fe-Mo-Y,
Fe-Nb-Ni, Fe-Nb-Ta, Fe-Nb-Ti, Fe-Nb-W, Fe-Nb-Y, Fe-Ni-Ta, Fe-Ni-Ti,
Fe-Ni-V, Fe-Ta-W, Fe-Ta-Y, Fe-Ti-V, Fe-Ti-W, Fe-Ti-Y, Fe-W-Y,
Fe-Y-Zr
Hf-Mo-Y, Hf-Nb-Zr, Hf-Ni-Ti, Hf-Ta-V, Hf-Ta-W, Hf-Ti-Zr
Solid carbides (30 phases):
WC MoC Mn7C3 Mn23C6 Mn5C2 Cr23C6 Cr7C3 Cr3C2
Sc3C4 Sc4C3 AlTi2C AlTi3C Co3AlC Cr2AlC Fe3AlC Hf2Al3C4
Hf3Al3C5 Hf5Al3C Mo3Al2C Mo3Ni3C Mo6Ni6C Nb2AlC Nb4Co2C Nb4Ni2C
Ta2AlC Ta4Co2C Ta5Al3C V2AlC Zr3Al3C5 Zr5Al3C
Solid nitrides (29 phases):
h-BN h-AlN YN WN_S1 Ti2N TaN_S1 Si3N4 ScN Mn4N Co4N Hf2N Hf3N2 Hf4N3 Mn6N4 Co2V4N Hf3AlN Hf5Al3N MnSiN2 Nb3Al2N Nb3Fe3N Nb4Co2N Nb4Ni2N Ni2V4N Ta4Ni2N TaMoN Ti2AlN Ti3AlN Zr3AlN Zr5Al3N
Solid borides (125 phases):
ZrB2 TiB2 HfB2 TaB2 NbB2 NiB Ni3B ZrB12 ZrB YB12 YB2 YB4 YB6 WB4 V3B4 VB VB2 V2B3 V3B2 Ti3B4 TiB TcB2 Tc7B3 Tc3B Ta3B2 TaB Ta3B4 Ta2B ScB12 ScB2 ReB2 Re3B Re7B3 NbB MoB4 Ni2B Ni4B3 Nb3B4 Nb3B2 NbB2 MoB2 MoB Mo2B Mo3B2 Mn2B MnB4 Mn3B4 MnB
MnB2 Fe2B FeB CrB Cr3B4 CrB2 CoB Co2B Co3B AlB2 CaB6 Cr2B Cr5B3 CrB4 FeB2 MgB2 MgB4 MgB7 Ti2B W2B AlCr2B2 AlCr3B4 Co20V3B6 Co21Cr2B6
CoVB3 AlCr3B4 CrSc2B6 AlFe2B2 Co21Hf2B6 Hf2Ni21B6 Hf9Mo4B HfCo3B2 Mo2Co21B6 Mo2CoB2 Mo2NiB2 Mo5SiB2 MoAlB MoCoB MoTiB2 MoYB4
Nb2Co21B6 Nb3Co4B7 Nb3Co5B2 NbFeB Ni20Al3B6 Ni21Sc2B6 Ni3Cr2B6 Ni6Si2B NiCr3B6 NiScB4 Re3Al2B Re4YB4 Re5Co2B4 ReCoB ReTi2B2 ReY2B6
ReY3B7 ReYB4 Ta2Co21B6 Ta2Ni21B6 Ta3Co5B2 W2Co21B6 W2CoB2 W2FeB2 W2NiB2 W3Hf9B2 WCoB WY3B7 Y5Si2B8 YCo12B6 YCo2B2 YCo3B2
YCo4B YCoB4 YCrB4 Zr2Co21B6 Zr2Ni21B6
Complete details on SpMCBN 8.0 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
SpMCBN contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys comprise the following systems:
The elements included in SpMCBN are:
Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Fe, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Re, Sc, Ta, Tc, Ti, V, W, Y, Zr
In FactSage 8.1 the database has been updated and new binary and ternary systems have been added.
The lists of the new and revised binary and ternary systems are as follows:
A spreadsheet listing all the SpMCBN 8.1 binary assessments has been prepared The reliability of the assessment for an individual binary or ternary system is summarized under "assessments"
in the documentation for the SpMCBN Database.
All the assessed systems are now presented with color-coding for the quality of the assessment,
in tables headed
Co-Cr-Fe, Co-Cr-Mo, Co-Cr-Ni, Co-Cr-Ta, Co-Cr-Zr, Co-Fe-Mn, Co-Fe-Mo,
Co-Fe-Nb, Co-Fe-Ni, Co-Fe-Ti, Co-Fe-Y, Co-Fe-Zr, Co-Mo-Ni, Co-Mo-W,
Co-Mo-Zr, Co-Nb-Ta, Co-Nb-W, Co-Ni-Re, Co-Ni-Ta, Co-Ni-Ti, Co-Ni-Y,
Co-Re-Y, Co-Ti-V, Co-Ti-Zr
Cr-Fe-Mn, Cr-Fe-Nb, Cr-Fe-Ti, Cr-Fe-Y, Cr-Fe-Zr, Cr-Hf-Ni, Cr-Hf-V, Cr-Hf-Zr,
Cr-Nb-Ni, Cr-Nb-V, Cr-Nb-W, Cr-Ni-Sc, Cr-Re-Ta, Cr-Re-W, Cr-Ti-V,
Cr-V-Zr, Cr-W-Zr
Fe-Hf-Y, Fe-Hf-Zr, Fe-Mo-Nb, Fe-Mo-Ta, Fe-Mo-Ti, Fe-Mo-V, Fe-Mo-Y,
Fe-Nb-Ni, Fe-Nb-Ta, Fe-Nb-Ti, Fe-Nb-W, Fe-Nb-Y, Fe-Ni-Ta, Fe-Ni-Ti,
Fe-Ni-V, Fe-Ta-W, Fe-Ta-Y, Fe-Ti-V, Fe-Ti-W, Fe-Ti-Y, Fe-W-Y,
Fe-Y-Zr
Hf-Mo-Y, Hf-Nb-Zr, Hf-Ni-Ti, Hf-Ta-V, Hf-Ta-W, Hf-Ti-Zr
Complete details on SpMCBN 8.1 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
SpMCBN contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys comprise the following systems:
The elements included in SpMCBN are:
Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Fe, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Re, Sc, Ta, Tc, Ti, V, W, Y, Zr
In FactSage 8.2 modelling of approximately 60 'end-members' associated with several different phases
has been completed to allow calculations for 4- or higher-component systems.
Such calculations should be viewed as interpolations of somewhat lower accuracy than that associated with the fully assessed lower-order systems.
In addition, a small adjustment to the assessed data for the liquid phase of the Nb-C system now avoids calculation of an inverse miscibility gap at very high temperatures in the liquid phase.
Complete details on SpMCBN 8.2 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
SpMCBN contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys comprise the following systems:
The elements included in SpMCBN are:
Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Fe, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Re, Sc, Ta, Tc, Ti, V, W, Y, Zr
In FactSage 8.3 now includes 2 new binary and 24 new ternary systems. These relate in all but two cases to systems with boron.
The calculations of thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams can be carried out for ca. 272 binary, and 585 ternary systems, for the individual temperatures or temperature ranges covered by the available experimental information.
Complete details on SpMCBN 8.3 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
SpMCBN contains assessed thermodynamic parameters for binary and ternary alloys of high-temperature materials containing carbon, nitrogen, boron, and silicon. The alloys comprise the following systems:
The elements included in SpMCBN are:
Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Fe, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, Re, Sc, Ta, Tc, Ti, V, W, Y, Zr
The SpMCBN database for FactSage 8.4 now includes nearly 100 new ternary systems. These relate to 33 systems with boron, 34 systems with carbon, 30 systems with nitrogen and 3 systems with silicon.
There are now 244 binaries and 712 ternaries that give a total of 956 phase diagrams stored in FactSage 8.4.
Complete details on SpMCBN 8.4 including all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.9
TDmeph is a special database developed for new generation nuclear fuels containing the following 14+2 elements:
In FactSage 8.0 the database has been updated and new binary and ternary systems have been added.
The lists of the new and revised systems are as follows:
Ba-O-Pu, Ba-Mo-O, C-Mo-U, C-O-U, C-Pu-U, Ce-Fe-O, Ce-O-Cs, Ce-O-Pu, Ce-O-U, O-Pu-U, C-Ru-U
Complete details on TDmeph including the revised documentation and all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
Minor update: In FactSage 8.1 the names of oxide end-members with non-stoichiometry in the solution phases have been improved.
TDNucl contains the following 18+2 elements:
It covers the entire field from metal to oxide domains.
In FactSage 8.0 the database has been updated and new binary and ternary systems have been added.
The lists of the new and revised systems are as follows:
Complete details on TDnucl including the revised documentation and all the phase diagrams are given in
Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu.
Minor update: In FactSage 8.1 the names of oxide end-members with non-stoichiometry in the solution phases have been improved.
Ag5Te3 AgBrCH5N AgBrH3N AgBrH9N3 AgCClH5N
AgCNO AgCNS AgC2H3O2 AgClH3N AgClH9N3
AgFH4O2 AgFH8O4 AgIO3 AgN3 Ag2O3
Ag2SO3 Ag2SeO3 Ag2SeO4 AlB3H12 AlB3H12
AlCH2NaO5 AlC3H9 AlCl6Fe AlH12N3O15 Al2C6H18
Al2H12O18S3 Al2Sr Al4Sr Al7Sr8 AmCl2
AmCl2 AmCl3 AmCl3 AmO AsO6Sb3
As2O6Sb2 As3O6Sb As4Se3 As4Se3 AuO4Re
B5Mo3 BCH3O BC2H7O2 BC2H7O2 BC3H9
BC3H9 BC3H9O3 BC3H9O3 BC4H14N BC6H15
BC6H15 BCl3H3P B13Mo6 B4S6 BaBr2H2O7
BaBr2H4O2 BaBr2O6 BaCl2H2O BaCl2H4O2 BaCl2H6O11
BaCl2O4 BaF6Si BaH18O10 BaH2I2O7 BaH2N6O
BaH8O12Re2 BaI2O6 BaO3Se BaO4Se BaO4SrTi
BaSe BeSe BeTe BiNa3O4 Bi2Te
C3Nb4 C5Pu6 C7Nb8 C7Pu8 C7V8
CNp CNb C2Th C2U C17U9
C2CaH2O5 Ca24Cu29O56 Ca10F2O24P6 CaCl2H12O6 CaCl2H8O8
CaFeO6Si2 CaH12I2O12 CaH4O5S CaH4O6Se CaH6O9P2
CaI2O6 CaO6P2 Ca12H14O31Si6 Ce4Ru3 Ce7O12
Ce6O11 Cl7Nb3 Cl8Nb3 CoSb Cr6S7
FeO FeSe Fe2Se2 Fe3Si7 FeTe
Mo9O26 NV2 NiSe Ni7Se8 NiTe
O8Pu5 O19W7 O3W O26W9 S2U

As the activity of Al2O3 is increased in a NaF-AlF3-CaF2 liquid solution,
the activity of Na2O will also increase according to reaction (1).
In the presence of CO2 in the gas at the anode, the activity of Na2CO3 will be
defined by reaction (2) at equilibrium.

[C3MIm], [C4MIm], [C3MPip],
[C3MPy], [C3MPyrr], [C4MPyrr], [C2Py], [C4Py]
Cl, Br, BF4, NO3, CH3SO3, PF6.
FTionx is included in the FACT 8.4 package of databases.
Complete details on FTionx including all the phase diagrams
are given in 'Documentation' in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
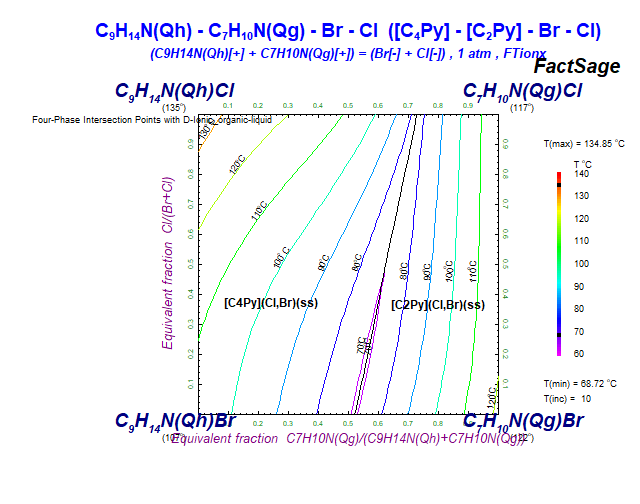
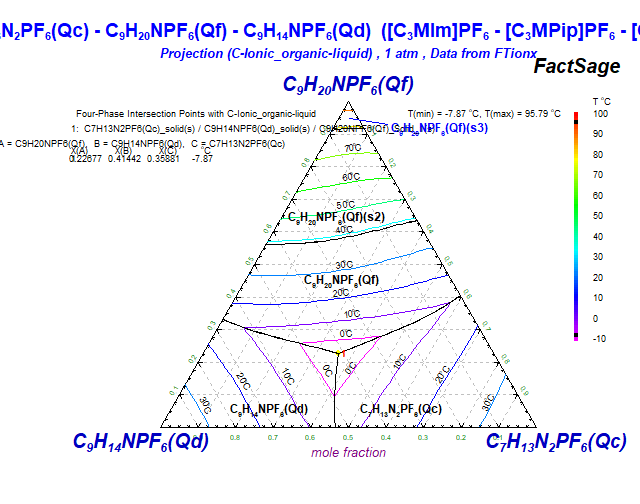
Ag, Al, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe,
Ga, Gd, Ge, H, Hf, Hg, Ho, In, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, N, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni,
O, P, Pb, Pr, S, Sb, Sc, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Ti, Tm, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr
Ag, Al, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Cr, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Gd, Ge, H, Ho, In, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Na, Nd, Ni, Pb, Pr, Sb, Sc, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Tb, Ti, Tm, V, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr


Solid carbides 23 phases:
WC, ZrC, Fe3C_S1, Ti2C, Ta2C, Nb2C, Mn7C3, Mn5C2, Fe5C2_S2, Fe7C3, Cr23C6, Cr7C3, Cr3C2, Cr3C, BaC2_S1, BaC2_S2, Cr2C, SrC2, AlTi2C, AlTi3C, Fe6W6C, Mn3AlC, Mn5SiC


FTlite 8.2 binary assessments
full size
Ag2O Al2O3 Al4C3 AlB2 AlCr2B2 AlCr3B4 AlN
BaB6 BaC2 BN CaB6 CaO Co2B Co3B
CoB CoN CoN3 Cr23C6 Cr2AlC Cr2B Cr2C
Cr2N Cr2O3 Cr3B4 Cr3C Cr3C2 Cr5B3 Cr7C3
CrB CrB2 CrB4 CrN Cu2O Fe2B Fe2N
Fe3B Fe3C Fe3O4_S1 Fe3O4_S2 Fe3O4_S3 Fe3O4_S4 Fe5C2
Fe6W6C Fe7C3 FeB GaN HfB2 InN K2O
KB6 Li2O LiB3 MgAl2O4 MgB2 MgB4 MgB7
MgO Mn23C6 Mn2B Mn2N Mn3AlC Mn3B4 Mn5C2
Mn5SiC Mn6N4 Mn7C3 MnB MnB2 MnB4 MnN
Mo2B Mo2C MoB MoB2 MoB4 MoC Na2C2
Na2O NaB15 Nb2AlC Nb2B3 Nb2C Nb3B2 Nb3B4
Nb5B6 NbB NbB2 Ni2B Ni3B Ni4B3' NiB
NiO Si3N4 SrB6 SrC2 Ta2C TaN Ti2AlC
Ti2C Ti2N Ti3AlC Ti2O Ti3B4 TiB TiB2
TiC TiN TiO V2AlC V2B3 V3B2 V3B4
VB VB2 VN W2B WB WC WN
ZrB ZrB12 ZrB2 ZrC ZrN
FTlite is designed for thermodynamic and phase equilibrium calculations involving
Al alloys, Mg alloys and Ti alloys.
It can also be used to perform calculations involving mixtures of Li-Na-KMg-Ca-Sr-Ba
with several other elements.


FTlite 8.3 binary assessments
full size
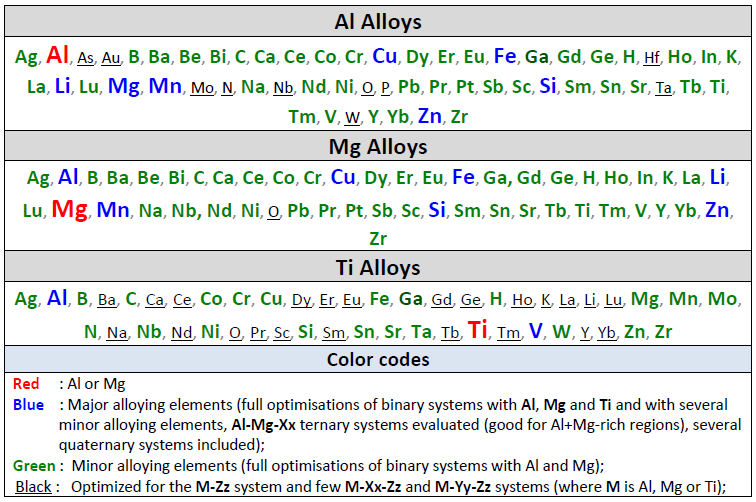

FTlite 8.4 binary assessments
full size
Liq(Matte/Metal) (MAT2): replaced by MAT2A, MAT2B and MAT2C
A major update for the S-Cu-Fe-Ni-Mn-Co-Cr system for calculation of equilibria among liquid and solid sulphide and metal phases. In the earlier versions of FactSage these calculations with Cu and Mn were not possible.
Pyrrhotite (PYRR): replaced by PYRRA, PYRRB and PYRRC
MS2_ solution: name changed to MeS2
M2S_ solution: name changed to M3S2
FCrS_ solution: replaced by the stoichiometric compound FeCr2S4
Fe9S_ solution: replaced by the stoichiometric compound Fe9S10
HCPS – eliminated
New components Sr and Cs have been added, and the interaction parameter C-Ti has been changed.
+ C, N, O, I
+ He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
Phase Names in the FToxid solution database in FactSage 5.5 that are no longer
in the FToxid solution database in FactSage 6.1
- All B2O3-containing sub-systems have been completely re-evaluated and re-optimized for all
compositions and all phases
- New B-containing melilite phase (gehlenite) (FToxid-Gehl)
- New compounds Ca2B2SiO7 and Ca11B2Si4O22
- New model for B-containing mullite. Former phases FToxid-MulB and FToxid-MULL
combined into FToxid-Mull
- Update of evaluation of boron in Ca2SiO4 (alpha and alpha-prime)
- Slag/glass phase re-evaluated and re-modeled. The charge compensation effect has been
taken into account.
- Compounds Na3BO3 and NaBSiO4 added
- Completely re-evaluated and re-optimized at all compositions and for all phases
The charge compensation effect has been taken into account for the liquid phase.
- Nepheline, carnegeite and NaAlO2 (FToxid-Neph, FToxid-Carn, FToxid-NASl and
FToxid-NASh) solutions are new, replacing the former stoichiometric compounds
NaAlSiO4 and NaAlO2.
- Evaluation/optimization updated
- Mn-Si-O and Mn-Fe-Si-O systems re-evaluated with the addition of trivalent Mn3+
(Mn2O3).
- New solution phases braunite and bixbyite added (FToxid-Brau and FToxid-Bixb).
- Slag, spinel and olivine phases updated as regards Mn
- FToxid-Rhod (rhodonite) updated to include FeSiO3 and MgSiO3 as components.
Former phase FToxid-MnPy has been merged into FToxid-Rhod
- Mn2O3 now a component of the corundum phase FToxid-Coru
- New tetragonal spinel phase (FToxid-TSPi) added. (Mn3O4 with Fe and Cr in
solution)
- New compounds Mn2O3 and MnO2
- New spinel phase FToxid-SPINB (FeO-CrO-MnO-Cr2O3-Fe2O3-Mn2O3)
- New (Mg,Cr)-olivine phase FToxid-OlivB.
- Systems TiO2-Al2O3-MO (M = Ca, Mg, Mn) re-evaluated and re-optimized
- Ti2O3 added as a component to the corundum FToxid-Coru phase
- Al added as a component to the titanium spinel phase (FToxid-TiSp)
- Former phases FToxid-MeO and FToxid-MONO have been merged into new
FToxid-MeO containing FeO-CaO-MgO-MnO-NiO-CoO + (Al, Fe(III),Cr,Zn in
dilute amounts)
- Completely re-evaluated and re-optimized using all available latest experimental data
and using a new model (Modified Quasichemical Model in the Quadruplet
Approximation) permitting calculations even to high sulphide contents.
Proto-pyroxene (pPyr): replaced by pPyrA, pPyrB and pPyrC
Update to FToxid-slag for more accurate calculation of copper and sulfur solubility in fayalite slags.
Clino-pyroxene (cPyr): replaced by cPyrA and cPyrB
Ortho-pyroxene (oPyr): will appear as a possible solution only if MgO is present
Mg-Zn pyroxene (MgPy): replaced by pPyrC
Ca3Al2Si3O12 CaAl2SiO6 CaFeSi2O6 Fe3Al2Si3O12 (FeO)2(TiO2) (FeO)(TiO2) FeSiO3_S1
FeSiO3_S2 FeSiO3_S3 Al2Fe2O6 Al2TiO5 Al4TiO8 Ca2FeSi2O7 Ca2Mg2Al28O46
Ca2MgSi2O7 Ca2Ti2O5_S1 Ca2Ti2O5_S2 Ca3Fe2Si3O12 Ca3MgAl4O10 Ca3Ti2O6 Ca3Ti2O7
Ca5Ti4O13 CaFe4O7 CaMg2Al16O27 CaSiTiO5 Fe2Al4Si5O18 FeTi2O4 Mg4Al10Si2O23
Mn2SiO4 Ca2Mn3O8 Ca2MnO4 Ca3Mn2O7 Ca4Mn3O10 CaMn2O4 CaMn3O6
CaMn4O8 CaMn7O12 CaMnO3 Cu2O K10Mg5Si11O32 K2Ca2Si2O7 K2Ca2Si9O21
K2Ca3Si6O16 K2Ca6Si4O15 K2CaSiO4 K2Mg5Si12O30 K2MgSi3O8_S1 K2MgSi3O8_S2 K2MgSi5O12
K2MgSiO4_S1 K2MgSiO4_S2 K2O K2Si2O5_S1 K2Si2O5_S2 K2Si2O5_S3 K2Si4O9_S1
K2Si4O9_S2 K2SiO3 K2Ti2O5 K2Ti2Si2O9 K2Ti3O7 K2Ti6O13 K2TiO3
K2TiSi2O7 K2TiSi4O11 K2TiSiO5 K4Ca3Al10O20 K4CaSi3O9 K4CaSi6O15 K4Mg2Si5O14
K4SiO4 K4TiO4 K6MgO4 K8CaSi10O25 K8Ti5O14 KAlO2_S1 KAlO2_S2
KMg2Al15O25 Mg2TiO4_S1 Mg2TiO4_S2 Mg6MnO8 MgTi2O5 MgTiO3 Mn2Al4Si5O18
Mn2O3_S1 Mn2O3_S2 Mn2TiO4_S1 Mn2TiO4_S2 Mn3Al2Si3O12 MnO2 MnSiO3
MnTi2O4 MnTi2O5 MnTiO3 Na10SiO7 Na2Al12O19 Na2Ca2Si2O7 Na2Ca3Al16O28
Na2Ca3Si6O16 Na2Ca8Al6O18 Na2CaSi5O12 Na2CaSiO4 Na2FeO2 Na2FeSiO4 Na2Mg2Si2O7
Na2Mg2Si6O15 Na2Mg5Si12O30 Na2MgSi4O10 Na2MgSiO4 Na2O_S1 Na2O_S2 Na2O_S3
Na2Si2O5_S1 Mg2TiO4_S1 Mg2TiO4_S2 Mg6MnO8 MgTi2O5 MgTiO3 Mn2Al4Si5O18
Na2Ti6O13 Na2Si2O5_S2 Na2Si2O5_S3 Na2SiO3 Na2Ti2O5 Na2Ti2Si2O9 Na2Ti3O7
Na3FeO3 Na2TiO3_S1 Na2TiO3_S2 Na2TiSi2O7 Na2TiSi4O11 Na2TiSiO5 Na3Fe5O9
Na4TiO4 Na4CaSi3O9 Na4Fe6O11 Na4FeO3 Na4Mg2Si3O10 Na4Mg3Si5O15 Na4SiO4
Na8Fe6Si15O40 Na5FeO4 Na5FeSi4O12 Na6Si2O7 Na6Si8O19 Na8Ca3Si5O17 Na8Fe2O7
NaFeSi2O6 Na8Ti5O14 NaAlO2_S1 NaAlO2_S2 NaFe2O3 NaFeO2_S1 NaFeO2_S2
Ti6O11 Ti10O19 Ti20O39 Ti3O5_S1 Ti3O5_S2 Ti4O7 Ti5O9
Ti7O13 Ti8O15 Ti9O17
Complete details on FToxid 8.3 including all the phase diagrams are given in the updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
TiO2-Ti2O3 + CaO-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-MnO-Mn2O3-Al2O3-SiO2
Rutile, Ilmenite, Pseudobrookite and Ti-spinel
Monoxide (Ti2O3 added), Corundum, Ca3Ti2O7-Ca3Ti2O6, Perovskite and Tetragonal-spinel
Complete details on FToxid 8.4 including all the phase diagrams are given in the updated Documentation in the FactSage Main Menu Window.
K2O-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2
SnO-SnO2 + MgO-CaO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2, SnO-SnO2-SiO2-ZnO, SnO2-ZrO2-TiO2
ZrO2-Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2
(Zr,Ti,Sn)O2 orthorhombic solution and Sn-spinel
Nepheline (KFeSi3O8 added); Leucite (KFeSi2O6 added); high-T Kalsilite (KFeSiO4 added);
high-T and low-T KAlO2-K2MgSiO4 solutions (KFeO2 added); Rutile and Corundum (SnO2 added);
cubic, tetragonal amd monoclinic ZrO2 (SnO2 and TiO2 added)
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Al, Fe(II), Fe(III), Co, Ni, Zn, Pb, La, Ce, Th,
U(III), U(IV), Pu(III), Pu(IV), Cr(II), Cr(III), Mo(V)
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Al, Fe(II), Fe(III), Co, Ni, Zn, Pb, La, Ce, Th,
U(III), U(IV), Pu(III), Pu(IV), Cr(II), Cr(III), Mo(V)
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Al, Fe(II), Fe(III), Co, Ni, Zn, Pb, La, Ce, Th,
U(III), U(IV), Pu(III), Pu(IV), Cr(II), Cr(III), Mo(V)
Ag2O AlCl3 CaAlCl5 CaFeCl5 CeCl3 CeF3 CoAl2Cl8
FeSiO3_S1 CoF2 CoFe2Cl8 CrAl2Cl8 CrCl2 CrCl3 CrF2
Cs3CeCl6 CsCe2Cl7 Cu2O FeAl2Cl8 FeCl2 FeCl3 K2CeCl5
K2CoCl4 K2FeCl4 K2O K2PbCl4 K2ZnCl4_S1 K2ZnCl4_S2 K3Ce5Cl18
K3CeCl6 K3Mn2Cl7 K4MnCl6 K5Zn4Cl13 KAlCl4_S1 KAlCl4_S2 KCoCl3
KFeCl3 KFeCl4_S1 KFeCl4_S2 KMnCl3 KNiCl3 KPb2Cl5 KZn2Cl5
LaF3 Li2CoCl4 Li2FeCl4_S1 Li2FeCl4_S2 Li2MnCl4 Li2NiCl4 Li4CoCl6
Li6FeCl8 Li6NiCl8 LiAlCl4 LiCoCl3 LiFeCl4 LuF3_S1 LuF3_S2
MgAl2Cl8 MgFe2Cl8 MgO MnAl2Cl8 MnCl2 MnF2_S1 MnF2_S2
MnFe2Cl8 Na2CoCl4 Na2FeCl4 Na2Mn3Cl8 Na2MnCl4 Na2NiCl4 Na2ZnCl4
Na2O_S1 Na2O_S2 Na2O_S3 Na3Ce5Cl18 Na6MnCl8 Na9Mn11Cl31 NaAlCl4
NaFeCl4 NaFeO2_S1 NaFeO2_S2 NaFeO2_S3 NaMn4Cl9 NiAl2Cl8 NiCl2
NiFe2Cl8 Rb2CeCl5 Rb3CeCl6 RbCe2Cl7 TiAl2Cl8_S1 TiAl2Cl8_S2 TiCl2
TiO_S1 TiO_S2 ZnCl2
MgCl2 PbCl2 MnCl2 CoCl2 NiCl2
In addition the updates to the database include the following changes.
The Li cation has been added to the SALTK liquid solution (which was originally Na, K // NO3, NO2, Cl, CO3, ClO4 in FactSage 8.1).
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Al, Fe(II), Fe(III), Co, Ni, Zn, Pb, La, Ce, Th,
U(III), U(IV), Pu(III), Pu(IV), Cr(II), Cr(III), Mo(V)
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Mn, Al, Fe(II), Fe(III), Co, Ni, Zn, Pb, La, Ce, Th,
U(III), U(IV), Pu(III), Pu(IV), Cr(II), Cr(III), Mo(V), Hg, Hg2
Ag, Al, As, Au, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ga, Ge, H, Hg, In, Li, Mg, Mn, Nb, Nd, Ni, O, P, Pb, Pd, Pt, Pr, S, Sb, Se, Si, Sn, Te, Ti, Tl, W, V, Zn, Zr.


FScopp 8.2 is a major update of the database.
A total of 545 binary systems (vs 422 in 8.2) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.

FScopp 8.2 binary assessments
full size

In FScopp 8.3 a total of 603 binary systems (515 in 8.2) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is shown here for the major and minor alloying elements of Cu-alloys.

FScopp 8.3 binary assessments
full size
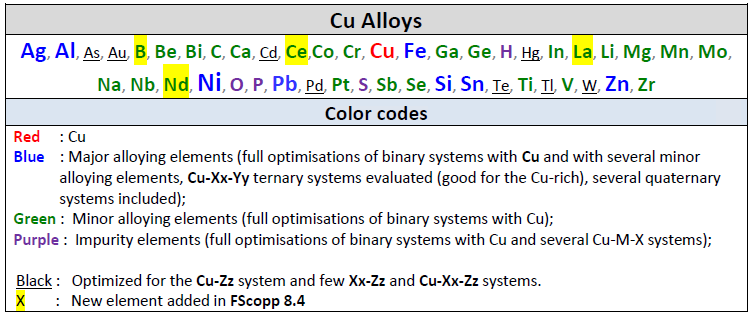
In FScopp 8.4 a total of 685 binary systems (603 in 8.3) have been evaluated,
for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.
A matrix of assessed binary systems is shown here for the major and minor alloying elements of Cu-alloys.
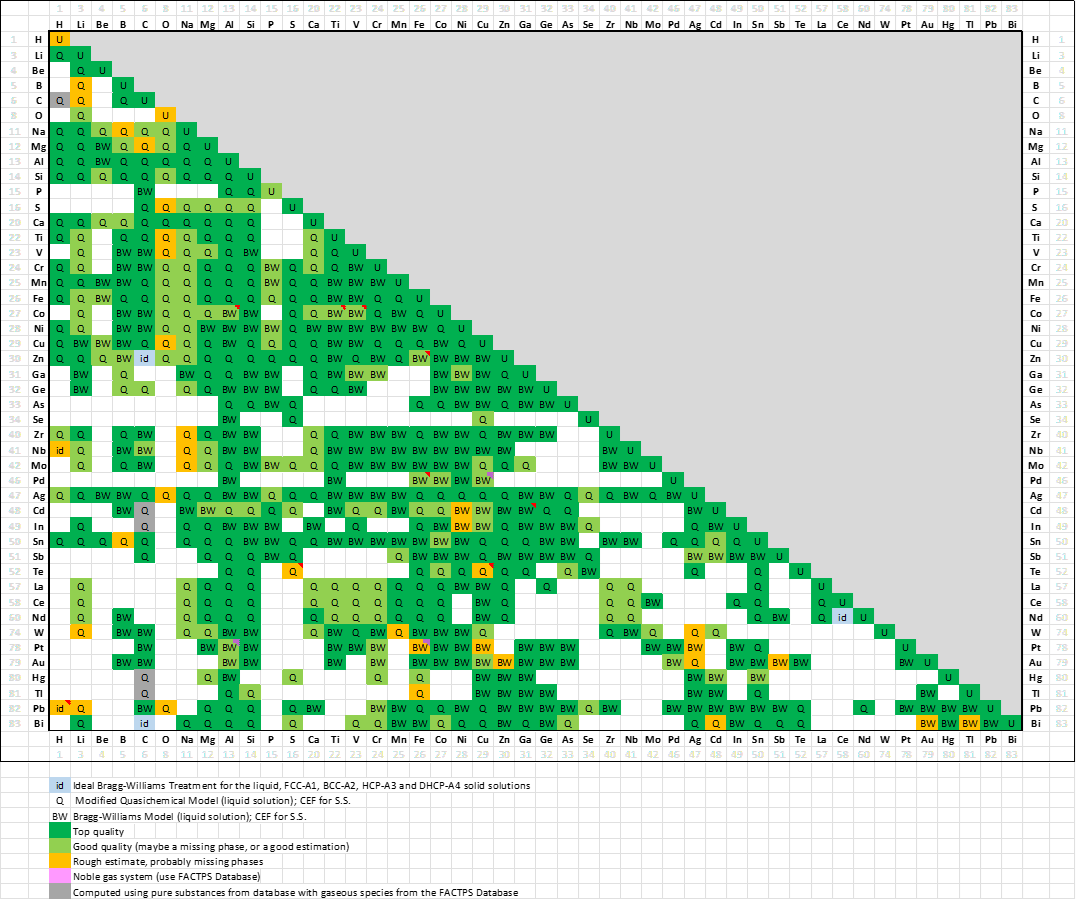
FScopp 8.4 binary assessments
full size
Ag, As, Au, Ba, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Cu, Fe, Ga, H, Hg, In, Ni, O, Pb, S, Sb, Se, Sn, Sr, Te, Tl, Zn

full size

FSlead 8.2 is a major update of the database.
A total of 253 binary systems (vs 161 in 8.1) have been evaluated, for most of them over the entire range of composition and for all stable phases.

FSlead 8.2 binary assessments
full size


FSlead 8.3 binary assessments
full size
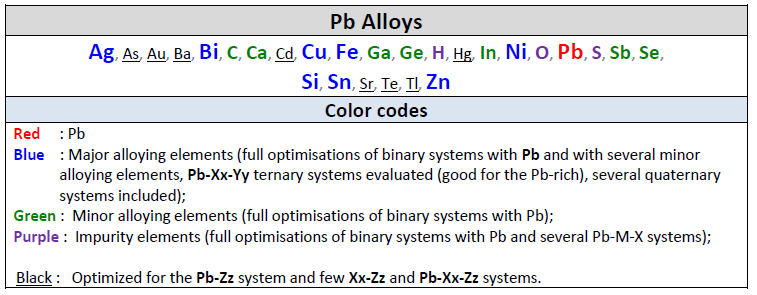
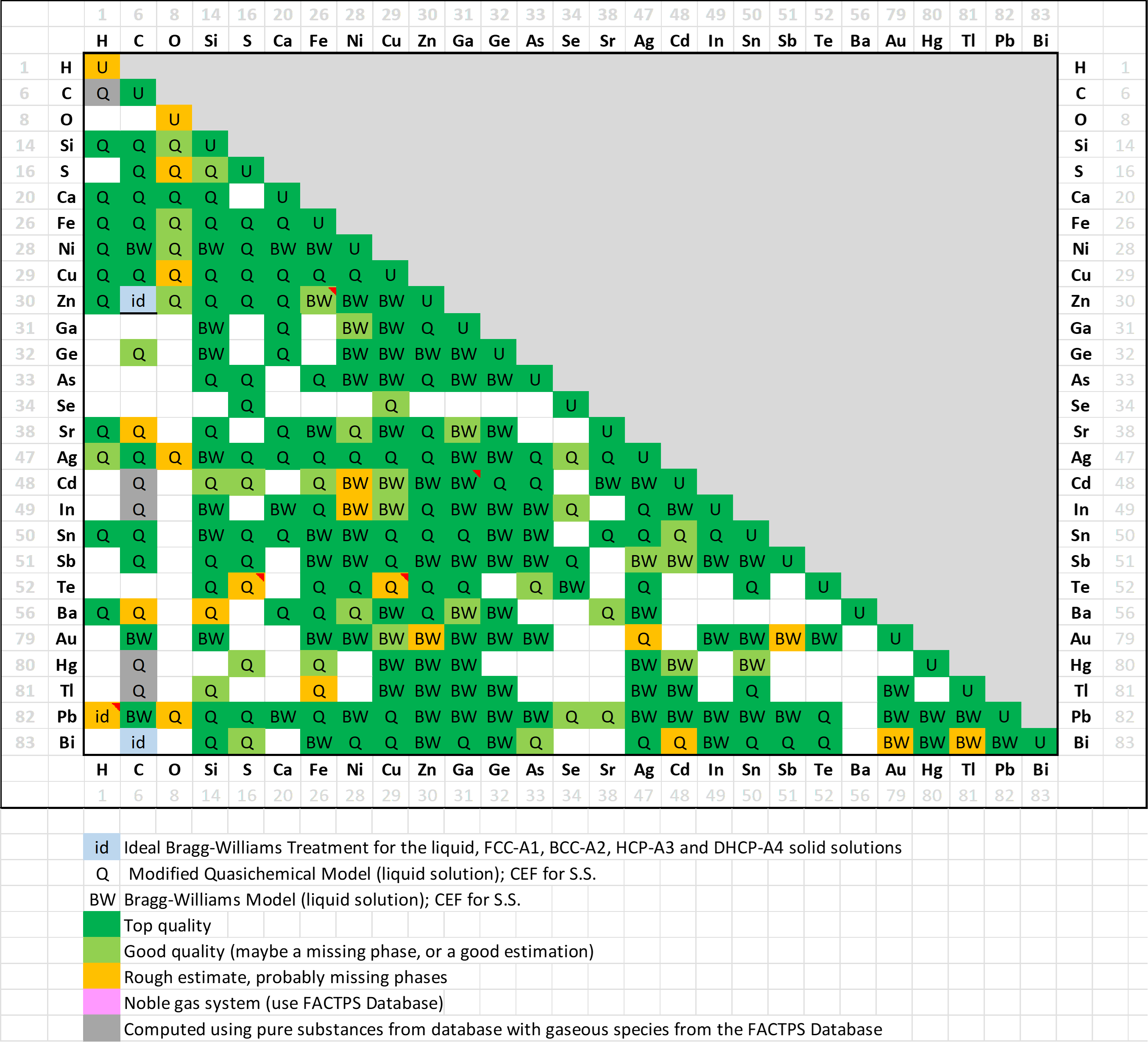
FSlead 8.4 binary assessments
full size
fcc: replaced by fcc1
The elements Hf and Ta have now been included in the updated version of the database.
This has resulted in the inclusion of assessed data for 7 new binary systems:
C-Hf, Hf-Ta, Hf-Ti, Hf-Ni, Ta-Ti, Si-Ta, Hf-Mo.
bcc: replacec by bcc1
hcp: replaced by hcp1
etc.
Al, B, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Mg, Mn, Mo,
N, O, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, S, Sb, Si, Sn, Ta, Ti, V, W, Zn, Zr
Al, B, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, H, Hf, La, Mg, Mn, Mo,
N, O, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, S, Sb, Si, Sn, Ta, Ti, V, W, Zn, Zr
Binaries: Al-P, Cr-P, Fe-P, Mn-P, Ni-P, Si-P
Ternaries: Fe-Mn-P, Al-Fe-P, Fe-Si-P, C-Fe-P, Cr-Fe-P, Fe-Ni-P
Binaries: Al-N, C-N, Si-N
Ternaries: Al-Fe-N, C-Fe-N, C-N-Si, Fe-N-Si, Mn-N-Si, Fe-Mn-N, Fe-N-P
Quaternaries: Al-Fe-N-Si, many quaternary systems with liquid only
Higher order system: Al-C-Fe-Mn-N-Si
Binaries: Al-Co (FCC is slightly changed)
Ternaries: Al-Co-Ni, Al-Cr-Ni, Al-Cr-Ti, Co-Cr-Ni, Co-Ni-Ti
Al, B, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, H, Hf, La, Mg, Mn, Mo,
N, O, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, S, Sb, Si, Sn, Ta, Ti, V, W, Zn, Zr
In summary, in FSstel the following systems have been updated
In FactSage 8.1 the FCC, BCC, Sigma and Laves C14 solutions in many ternary
and multicomponent systems
including the Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni-V-W system have been added or updated for the
high alloyed steel applications and high entropy alloys (HEAs) applications.
Al-Hf, B-Si, Bi-Cu, Bi-Sn, C-Ca, Co-Mg, Co-P, Co-V, Co-Zn, Co-Zr, Cr-Sn, Cu-W, Fe-Hf, Hf-Si, Mg-Ni, Mg-Sn,
Mg-Zn, Mn-Mo, Mn-Nb, Mn-W, Ni-Sn, Nb-Ta.
Al-Nb, Co-N, Fe-Mo, Mo-V, Ni-Sn, Sb-Zn, Ta-V, W-Zr, etc.
Al-Fe-Zr, C-Co-V, C-Cr-Mn, C-Cr-Mo, C-Cu-Fe, C-V-W, C-W-Zr, Co-Cr-Fe, Co-Cr-V, Co-Fe-V, Co-Fe-Zn, Co-Ni-V,
Co-N-W, Cr-Fe-Mo, Cr-Fe-W, Cr-Mn-Ti, Cr-Mo-Ni, Cr-Ni-W, Cu-Fe-Ni, Fe-Mn-Nb, Fe-Ni-Si, Fe-Ni-Zr, Mo-N-Nb, etc.
FSstel covers a wide range of commercial grade carbon steels and stainless steels, and new high advanced steels under development.
Al, B, Bi, C, Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, H, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, O, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, S, Sb, Si, Sn, Ta, Ti, V, W, Zn, Zr,
RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu)
In summary, in FSstel the following systems have been added or updated.
In FactSage 8.2 numerous binary rare-earth systems Fe-RE, Mn-RE, Co-RE, Ni-RE, Si-RE, Al-RE, and Mg-RE
have been added. Many key binary, ternary and multi-component systems covering the Fe-Cr-Mo-Nb-Ni-Ta have been added or updated for improved phase diagram calculations in super alloys.
a. Fe-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Gd, Ho, La, Lu, Nd, Pr, Sc, Sm, Tb, Tm, Y)
b. Mn-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Gd, Ho, La, Lu, Nd, Pr, Sc, Sm, Tb, Tm, Y)
c. Co-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Gd, Ho, La, Nd, Pr, Sm, Y)
d. Ni-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Gd, Ho, La, Nd, Pr, Sm, Tb, Y)
e. Si-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Gd, Ho, La, Nd, Pr, Sc, Sm, Tb, Tm, Y)
f. Al-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, Lu, Nd, Pr, Sc, Sm, Tb, Tm, Y, Yb)
g. Mg-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Nd, Pr, Tb)
a. New Fe-Nd-Dy-B quaternary system including small amount of Pr, Tb, Cu, Ni, Co, etc.,
and reaction with liquid Mg.
b. B-Sn, B-Pb, B-Zn, B-Dy, B-Tb, B-Pr, B-Nd, B-Mg, Mg-Ni, etc.
a. New update of existing binary system: Mo-Ni, Fe-Ta, Ni-Ta, etc.
b. New ternary systems: Cr-Nb-Ni, Mo-Ni-Ta, Fe-Ni-Ta, Mo-Nb-Ni
Al, B, Bi, C, Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, H, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, O, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, S, Sb, Si, Sn, Ta, Ti, V, W, Zn, Zr,
RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu)
FSstel contains 379 completely assessed 61 partially assessed binary alloy systems,
together with approximately 158 ternary and 28 quaternary systems for which assessed parameters are available for phases of practical relevance.
It contains 186 solution phases and 1014 stoichiometric compounds.
a. Cr-RE (RE = Ce, Dy, Er, Eu, Gd, Ho, La, Lu, Nd, Pr, Sc, Sm, Tb, Y, Yb)
a. Ca containing system: Ca-Co, Ca-Cr, Ca-Mo, Ca-Ni, Ca-P, Ca-Sn, Ca-Ta, Ca-Ti, Ca-V, Ca-W
b. Mg containing system: Mg-Mo, Mg-P, Mg-Ta, Mg-W
c. Sc containing system: Sc-Co, Sc-Mo, Sc-Ni, Sc-V
d. Zn containing system: Zn-Mo, Zn-Ni, Zn-S, Zn-Ti, Zn-V, Zn-W, Zn-Y, Zn-Zr
a. Sn-S, Mo-Pb, Cu-Mo, Cu-Nb
a. Fe-Zn-S, Fe-Zn-Zr, Al-Nb-Ni
Al, B, Bi, C, Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, H, Hf, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, O, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, S, Sb, Si, Sn, Ta, Ti, V, W, Zn, Zr,
RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu)
(a) Binary systems
Fe-Mo system: change of Mu_phase
Co-Nb system: replacement of CONB_lambda phase with Laves_C15, and
replacement of CONB_Mu phase with Mu_phase
Nb-Ni system: replacement of Nb6Ni7 phase with Mu_phase
Fe-Nb system: update of Mu_phase, Laves_C14, liquid phase
Ni-Ta system: update of Mu_phase
Fe-Ta system: update of Mu_phase
Fe-Mo-Ni system: update of Mu_phase
Co-Mo-Ni system: update of Mu_phase
Co-Cr-Mn system: update of Sigma, High_Sigma, Cub_A13, HCP
Cr-Mn-Ni system: update of BCC, FCC, Liquid
Co-Cr-Fe system: update of BCC
Co-Fe-Mn system: update of CBCC
Co-Cr-Ni system: update of Sigma, FCC, BCC, Liquid, P_phase
Fe-Ni-Ta system: update of Mu_phase, Liquid, others.
Co-Fe-Nb system: update of Mu_phase, Liquid
Cr-Nb-Ni system: update of Mu_phase, Liquid
Fe-Nb-Ni system: update Mu_phase, Liquid
Co-Cr-Fe-Mn system: high-Sigma solution containing Co
Al-V-H, Co-V-H, Fe-V-H, and Ni-V-H systems
C, N and H are added to these ordered phases
Fe-P-X ternary system: update for Fe3P in Me3P solid solution
Cu-O system: update of oxygen solubility in liquid Cu
Oxygen containing system: oxygen solubility in FCC and BCC solutions: change
of the solubility limits of oxygen in the solid solutions (max. 10 mol %)
Ni-P-S system: addition of NiPS3 compound
Cr-Ni system: small modification of liquid phase
Co-Cr system: small modification of liquid phase
Cr-Ta system: small modification of liquid phase
Cr-Ti system: correction of Laves_C14 and C36 (remove C-TiCr2 phase and combine it to C14)
Ag, Al, Am, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, Hf, Hg, Ho, In, Ir, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni, Np, O, Os, P, Pa, Pb, Pd, Pr, Pt, Pu, Rb, Re, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Tc, Te, Th, Ti, Tl, Tm, U, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr
Ag, Al, Am, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, H, Hf, Hg, Ho, In, Ir, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni, Np, O, Os, P, Pa, Pb, Pd, Pr, Pt, Pu, Rb, Re, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Tc, Te, Th, Ti, Tl, Tm, U, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr
Ag, Al, Am, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, H, Hf, Hg, Ho, In, Ir, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni, Np, O, Os, P, Pa, Pb, Pd, Pr, Pt, Pu, Rb, Re, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Tc, Te, Th, Ti, Tl, Tm, U, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr
Ag, Al, Am, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, H, Hf, Hg, Ho, In, Ir, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni, Np, O, Os, P, Pa, Pb, Pd, Pr, Pt, Pu, Rb, Re, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Tc, Te, Th, Ti, Tl, Tm, U, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr
Ag, Al, Am, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, H, Hf, Hg, Ho, In, Ir, K, La, Li, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Na, Nb, Nd, Ni, Np, O, Os, P, Pa, Pb, Pd, Pr, Pt, Pu, Rb, Re, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Tc, Te, Th, Ti, Tl, Tm, U, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn, Zr
- the solubility of Au in Ge (DIAMOND_A4) is now in accordance with SGTE 2017
- RHOMBOHEDRAL_A7: As,Bi and Sb now have the same stabilities as in their pure stable states
- the end member Au2Bi in Au2Bi_C15 and Au2Bi(s) now have the same stability
- the elements Ba and Ca have been added to the BCC_A2 solution phase and Ca has been added to the FCC_A1 solution phase as well
- for the systems Ba-Ru and Ca-Ru an artificial phase stablity of the BCC_A2 phase has been corrected.
The same has been done for CUB1 (CUB_A13) in the Ag-Co system.
- Two new solution phases have been introduced:
BETA_RHOMBO_B corresponding to B(s) with solubility for Mn (in accordance
with SGTE2017),
GRAPHITE, pure C with solubility for B (in accordance with SGTE2017).

full size
B-C-Cr B-C-Hf B-C-Mo B-C-Nb B-C-Ni B-C-Sc B-C-Si B-Co-Cr B-Co-Hf
B-Co-Mo B-Co-N B-Co-Nb B-Co-Re B-Co-Si B-Co-Ta B-Co-V B-Co-W
B-Co-Y B-Co-Zr B-Cr-Fe B-Cr-N B-Cr-Sc B-Cr-Y B-Fe-Hf B-Fe-N B-Fe-Sc
B-Hf-Re B-Mo-N B-Mo-Y B-N-Nb B-N-Ni B-N-Ta B-N-Y B-Ni-Re B-Ni-Sc
B-Re-Sc B-Re-Si B-Re-Ta B-Re-Ti B-Re-V B-Re-Y B-Re-Zr B-Sc-W B-Sc-W
B-Si-Y B-W-Y
C-Co-Hf C-Co-Nb C-Co-Si C-Co-Ta C-Co-Ti C-Co-V C-Co-Zr C-Cr-Hf C-Cr-N
C-Cr-N C-Cr-Re C-Fe-Hf C-Hf-N C-Hf-Re C-Mo-Re C-N-W C-Nb-Re C-Re-Si
C-Re-Ta C-Re-Zr C-Sc-Ti C-Sc-Zr C-Si-Ta
Co-Mo-Si Co-N-Nb Co-N-Si Co-N-V Co-Nb-Si Co-Sc-Si Co-Si-Ti Co-Si-W
Cr-Fe-Si Cr-Hf-N Cr-N-Ti Cr-Sc-Si Cr-Si-Y
Fe-Mn-Si Fe-Mo-N Fe-N-Nb Fe-N-Ti Fe-N-W
Hf-N-Si
Mo-N-Ni Mo-N-V Mo-Si-Y
N-Nb-Si N-Nb-Ta N-Ta-Ti N-Si-Ta N-Si-Ti N-Si-Y N-Si-Zr
Nb-Si-V
Ni-Re-Si
Re-Sc-Si Re-Si-Y
Sc-Si-Ta Sc-Si-V Sc-Si-W
C-Ca, Mn-Si
A spreadsheet listing all the SpMCBN 7.3 binary assessments has been prepared that
summarises the quality of the evaluations (top, good or poor).
'Documentation > [SpMCBN] > Spreadsheet of binary assessments ...'
'View Data > Data compound > SpMCBN > Elements: ALL > Assessments ...'

B-C-Fe, B-N-Al, B-N-Mn, B-N-Re, B-N-Sc, B-Si-Mn, C-N-Si, C-Si-Mn,
N-Si-Mn, N-Si-Re, N-Si-Sc, Co-Cr-Re, Cr-Mo-Nb, Cr-Mo-Ni, Cr-Mo-Ta,
Cr-Mo-Ti, Cr-Mo-V, Cr-Mo-Zr, Cr-Nb-Ta, Cr-Nb-Ti, Cr-Nb-Zr, Cr-Ni-Re,
Cr-Ni-Ti, Cr-Re-Ta, Cr-Ta-Ti, Cr-Ta-V, Cr-Ta-W, Cr-Ta-Zr, Cr-Ti-Zr,
Cr-V-W
Me1-Me2-C, Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si, Me-B-Si, Me1-Me2-Me3
B, C, N, Si with
Co-Nb, Co-Zr, Fe-Hf, Fe-Nb, Fe-Re, Fe-Tc, Ni-Ta, Re-W
'Documentation > [SpMCBN] > Spreadsheet of binary assessments ...'
'View Data > Data compound > SpMCBN > Elements: ALL > Assessments ...'

Al-Fe-Mn
A further development of the SpMCBN Database in FactSage 8.1 is represented by the introduction of
volumetric and thermal conductivity parameters for 184 pure solid phases. Volumetric properties (density at 298.15K, volumetric thermal expansivity, compressibility and derivative of the Bulk Modulus) and thermal conductivity parameters (based on the Debye Temperature, Gruneisen Parameter, and atoms per crystallographic cell) are now available for the following carbides, nitrides and borides:
(In order to calculate these properties you must select the "use V & physical property data" option in the Equilib Menu Window.)
The total number of stored SpMCBN phase diagrams is now 740 (cf. 664 in 7.3)
Me1-Me2-C, Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si, Me-B-Si, Me1-Me2-Me3
B, C, N, Si with
Co-Nb, Co-Zr, Fe-Hf, Fe-Nb, Fe-Re, Fe-Tc, Ni-Ta, Re-W
SpMCBN Binary Assessments
- see the partial listing on the right
- see the partial listing on the right
For a complete listing of all the SpMCBN Binary Assessments click
all listings


Al-Fe-Mn
The total number of stored SpMCBN phase diagrams is now 837 (cf. 740 in 8.0)
Me1-Me2-C, Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si, Me-B-Si, Me1-Me2-Me3
B, C, N, Si with
Me1-Me2-C, Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si, Me-B-Si, Me1-Me2-Me3
B, C, N, Si with
C-N, C-Y
B-Al-Mn, B-Al-Y, B-C-Ni, B-C-Y, B-Co-Fe, B-Co-Mn, B-Co-Ni, B-Co-Sc, B-Co-Ti, B-Cr-Mn, B-Cr-Re, B-Fe-Mn, B-Fe-Mo, B-Fe-Ni, B-Fe-Re, B-Fe-Y, B-Mo-Re,
B-Nb-Re, B-Ni-Y, B-Re-W, B-Sc-V, C-Co-Y, C-Fe-Y, C-Ni-Y
Me1-Me2-C, Me1-Me2-N, Me1-Me2-B, Me1-Me2-Si, Me-C-N, Me-C-B, Me-C-Si, Me-N-B, Me-N-Si, Me-B-Si, Me1-Me2-Me3
B, C, N, Si with
O, U, Pu, Zn, Fe, Si, C, Ba, Ce, Cs, La, Mo, Ru, Sr + Ar, H.
Ba-Ce, C-Ce, C-Cs, C-Pu, C-Sr, C-U , Ce-Cs, Ce-Fe, Ce-La, Ce-Mo, Ce-O, Ce-Pu, Ce-Ru, Ce-Si, Ce-Sr, Ce-U, Ce-Zr, La-Ru, Mo-O, Mo-Pu, O-Pu, Ru-U
BaO-CeO2, BaO-ZrO2, CeO2-La2O3, CeO2-SrO, Ce2O3-MoO3, Ce2O3-SiO2, CeO2-ZrO2, Ce2O3-ZrO2, La2O3-ZrO2, PuO2-ZrO2, PuO2-UO2
Ce-O-Pu, Fe-O-Pu, La-O-Pu, Mo-O-Pu, O-Pu-Si, O-Pu-Sr, O-Pu-Zr, C-O-Pu
O, U, Zr, Ag, In, B, C, Fe, Cr, Ni, Ba, La, Sr, Ru, Al, Ca, Mg, Si + Ar, H
Ag-Al, Ag-B, Ag-C, Al-Ca, Al-Cr, Al-In, Al-Zr, B-C, B-La, B-Ru, C-Ca, C-Cr, C-Mg, C-Ni, C-Sr, C-U, Ca-Mg, Cr-La, Cr-O, In-Zr, La-Ni, La-Ru, Ni-Sr, Ni-Zr, O-U, Ru-U
Al2O3-CaO, BaO-ZrO2, La2O3-ZrO2
Al-O-Fe, C-O-U, Ca-Cr-O, Cr-O-Si, Ni-O-Si
Al2O3-CaO-MgO, Al2O3-MgO-SiO2, CaO-FeO-Fe2O3, CaO-MgO-SiO2, SiO2-FeO-Fe2O3
Al-Ca-Fe-O, Al-Fe-O-Si, Ca-Cr-O-Si
Screenshot showing the summary of public databases in FactSage 8.4.